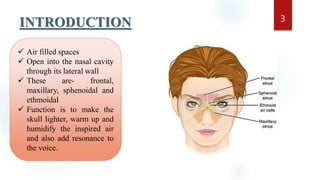
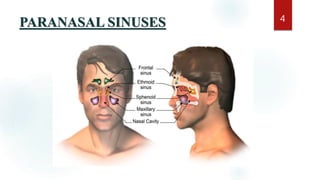
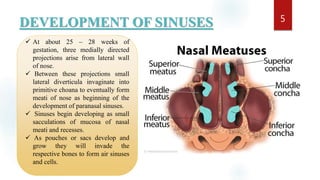
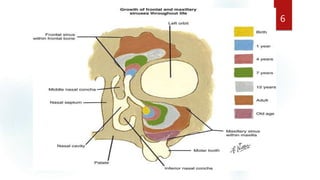
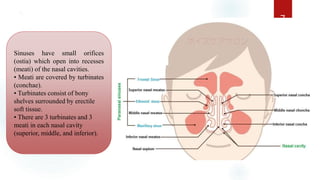
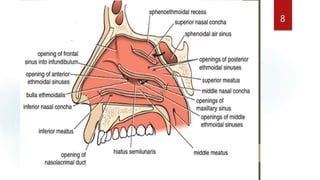
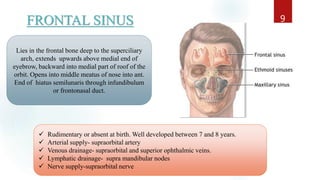
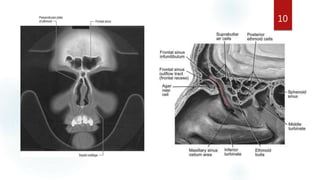
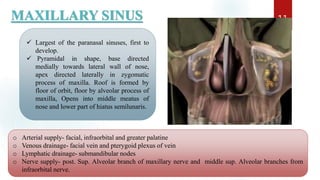
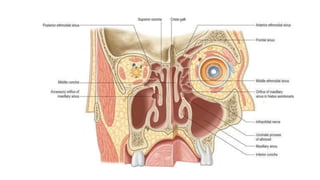
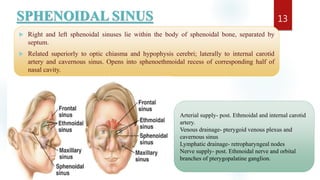
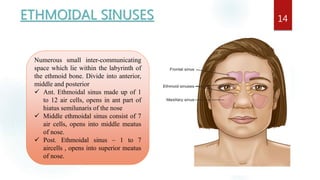
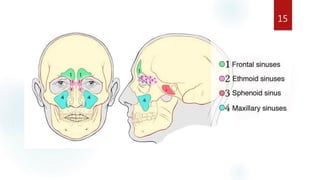
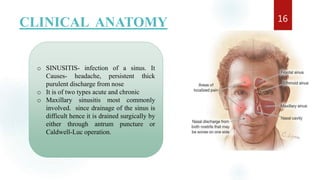
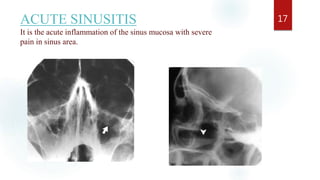
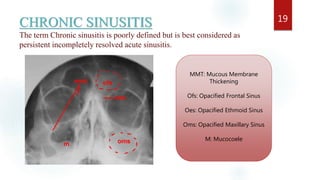
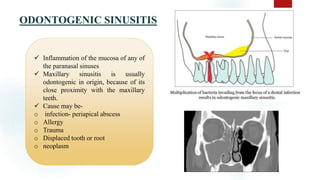
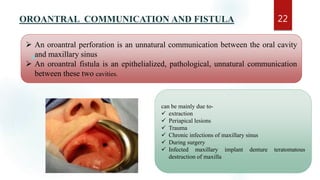
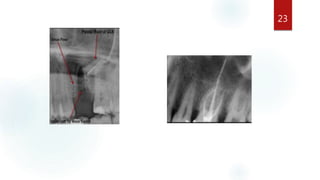
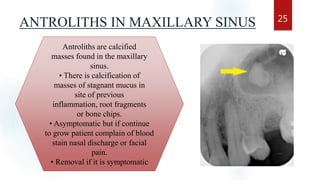
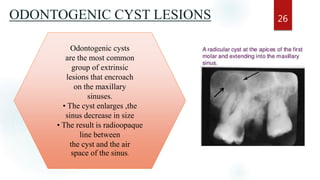
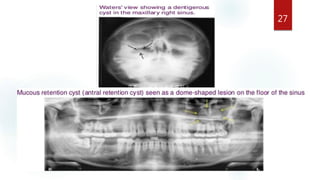
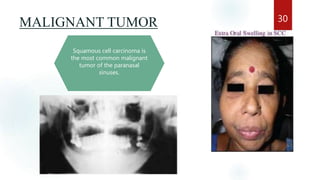
The document discusses the paranasal sinuses. There are four pairs of paranasal sinuses located around the nasal cavity that develop from invaginations of the nasal cavity mucosa into the bones. The maxillary sinus is the largest sinus and most clinically relevant as it is close to the teeth. Sinusitis is inflammation of the sinuses which can be acute or chronic and is usually caused by infection, trauma, dental issues or tumors. Anatomical relationships between the sinuses and structures like the orbit and teeth are important for dentists to understand.