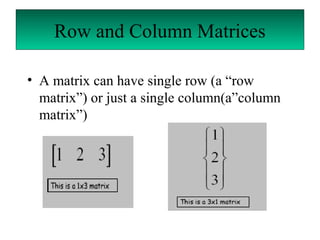
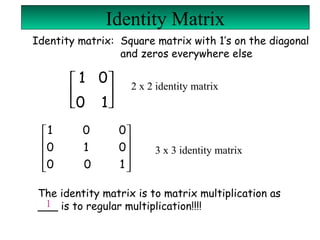
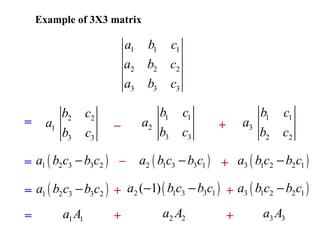
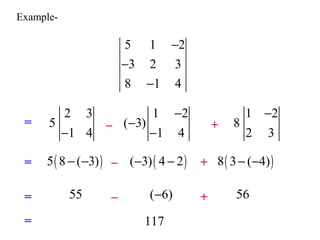
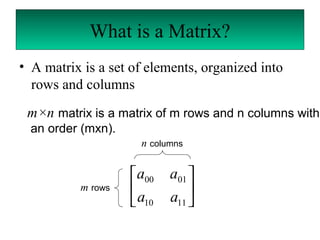
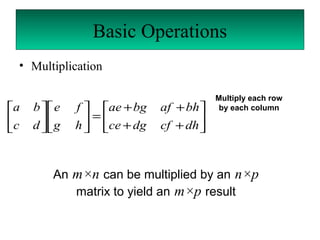
A matrix is a set of elements organized into rows and columns. Basic matrix operations include addition, subtraction, and multiplication. A matrix can be multiplied by another matrix if the number of columns of the first equals the number of rows of the second. The determinant of a matrix is a value that is used to determine properties of the matrix such as invertibility. Cramer's rule can be used to solve systems of linear equations involving matrices.

![Matrix aarriitthhmmeettiicc ((ooppeerraattiioonnss))
Matrix Addition/Subtraction
MMaattrriixx aaddddiittiioonn.. AAmm´nn aanndd BBmm´nn
• mmuusstt hhaavvee tthhee ssaammee nnuummbbeerrss ooff rroowwss aanndd
ccoolluummnnss
• aadddd ccoorrrreessppoonnddiinngg eennttrriieess
AAmm´nn ++ BBmm´nn == CCmm´nn == [[aaii,,jj ++ bbii,,jj]]
ù
ú ú ú
û
1 1
é
=
1 3
ê ê ê
ë
0 2
3,2 A
ù
ú ú ú
û
é
ê ê ê
ë
4 5
1 6
-
= -
2 3
3,2 B
ù
ú ú ú
û
é
ê ê ê
5 6
+ = -
ë
1 8
3 0
3,2 3,2 A B
MMaattrriixx ssuubbttrraaccttiioonn iiss ddoonnee ssiimmiillaarrllyy](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/matrices2-140903093717-phpapp01/85/Matrices-3-320.jpg)

![Basic Operations
• Transpose: Swap rows with columns
ù
ú ú ú
û
a b c
é
=
g h i
ê ê ê
ë
d e f
M
ù
ú ú ú
û
a d g
é
=
c f i
ê ê ê
ë
b e h
MT
ù
ú ú ú
V V T = [x y z]
û
x
é
=
z
ê ê ê
ë
y](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/matrices2-140903093717-phpapp01/85/Matrices-6-320.jpg)