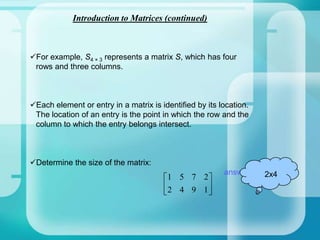
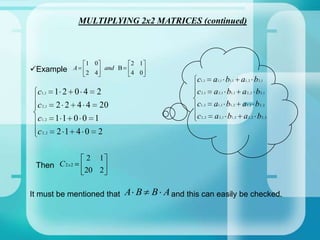
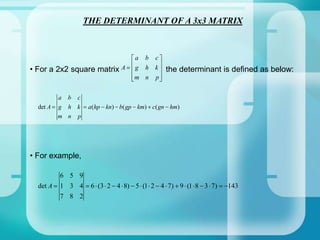
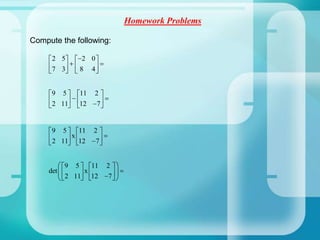
The document provides an introduction to matrix operations including addition, subtraction, multiplication, and determinants. It defines what a matrix is and how they are represented and sized. It then explains how to perform addition and subtraction of matrices by adding or subtracting the corresponding entries. Matrix multiplication is defined as being possible only when the number of columns of the first matrix equals the rows of the second. Determinants are explained as being unique to square matrices, and formulas are given for finding the determinants of 2x2 and 3x3 matrices. Homework problems are assigned involving computing various matrix operations.