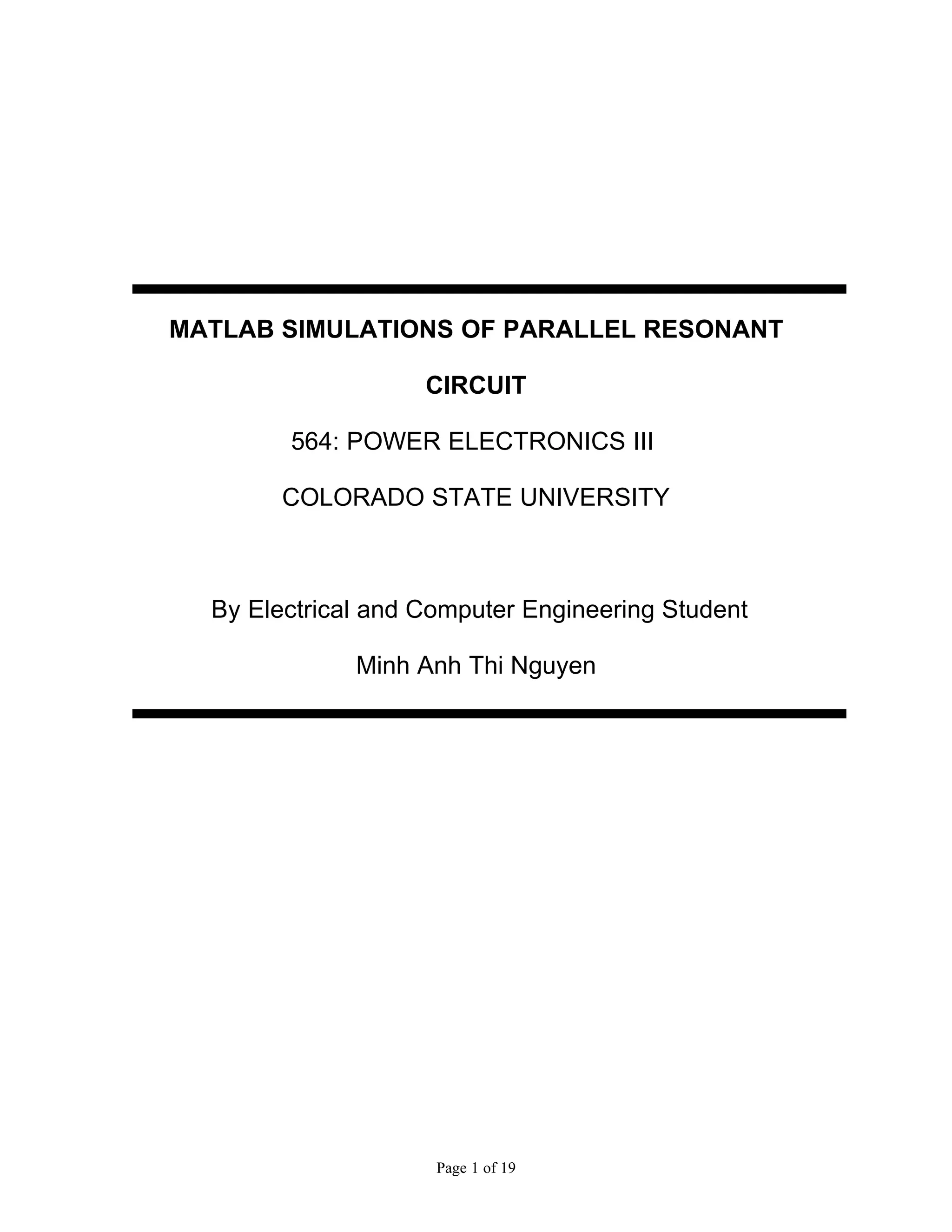
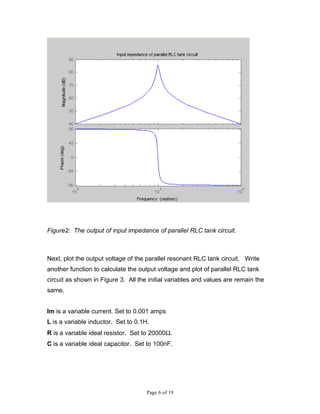
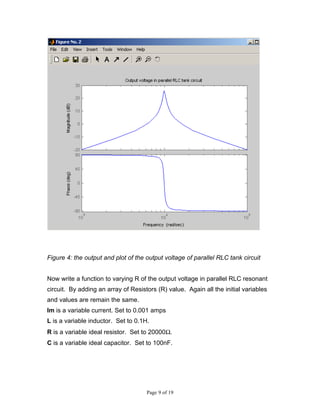
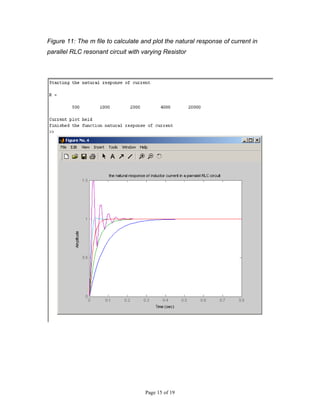
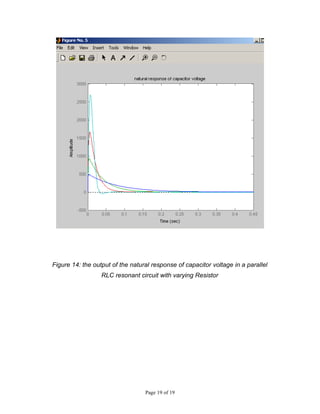
This document describes MATLAB simulations of parallel resonant circuits. It provides instructions for writing MATLAB functions to calculate the input impedance, output voltage, natural current response, and natural voltage response of parallel RLC circuits. The functions vary resistor values in the circuit and plot the results. The purpose is for students to better understand characteristics of parallel resonant circuits through MATLAB simulation and function writing.