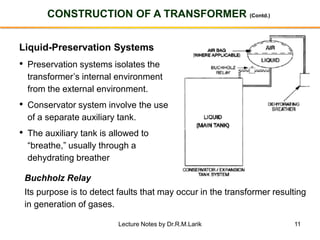
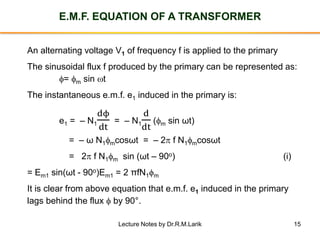
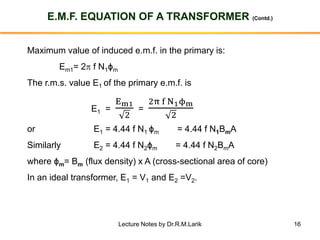
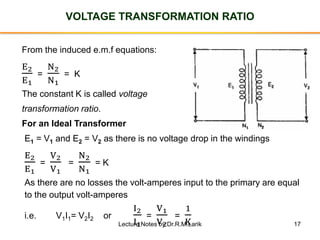
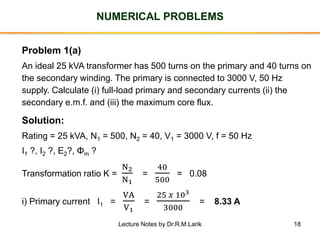
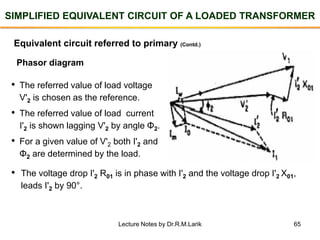
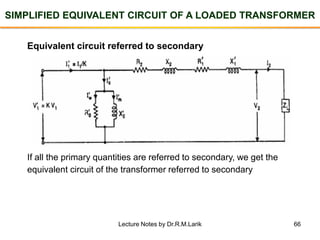
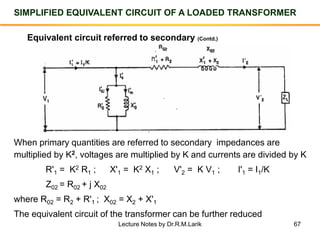
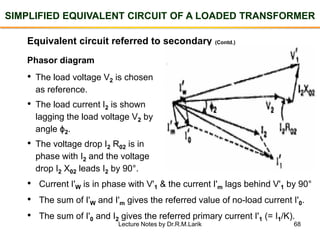
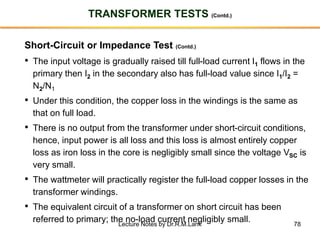
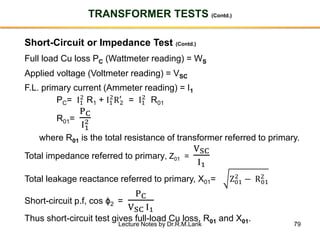
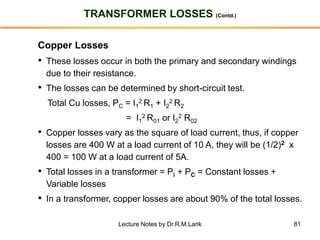
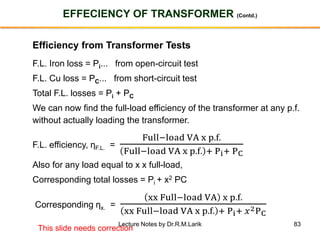
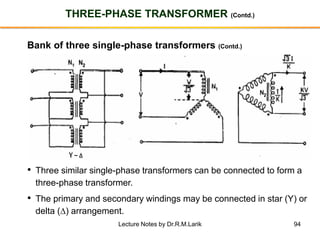
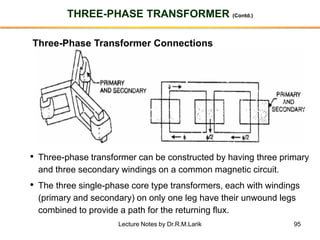
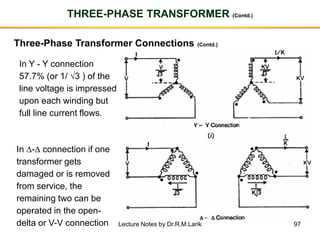
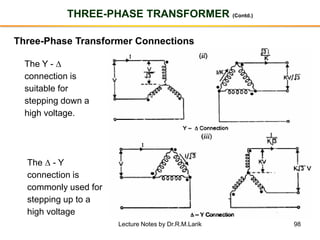
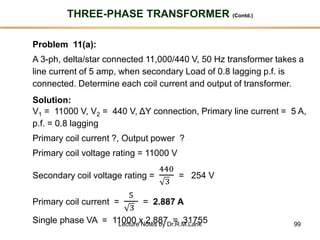
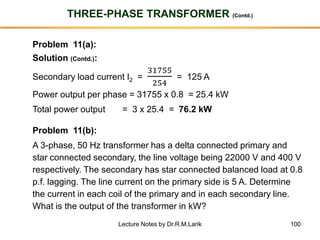
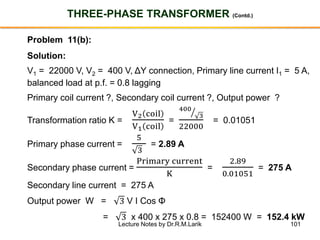
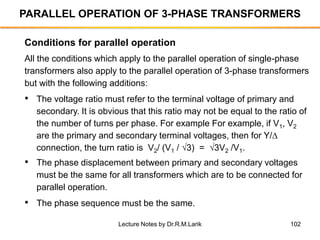
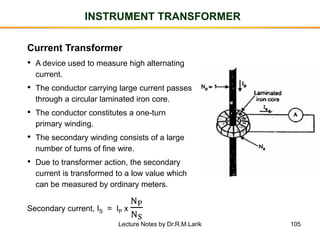
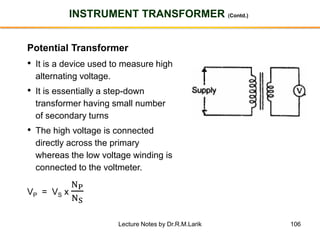
The document provides information about transformers, including:
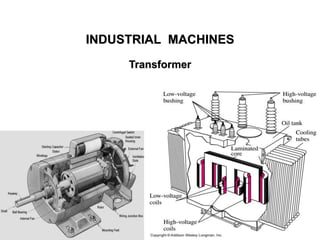
- Transformers can change the magnitude of alternating voltage or current from one value to another using electromagnetic induction. They have no moving parts and are rugged and durable.
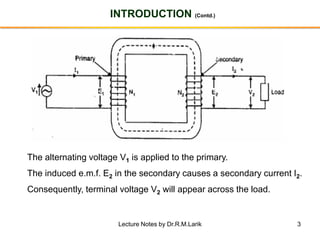
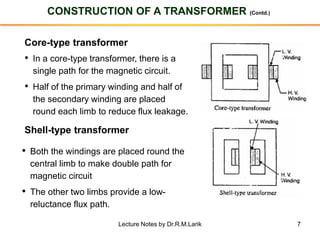
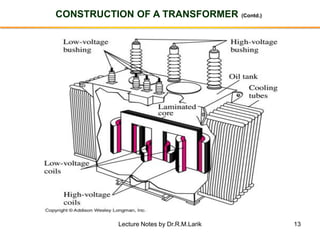
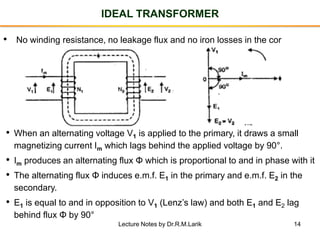
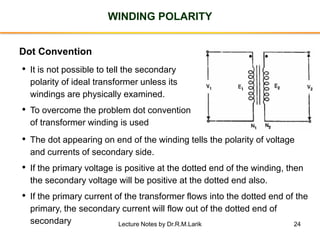
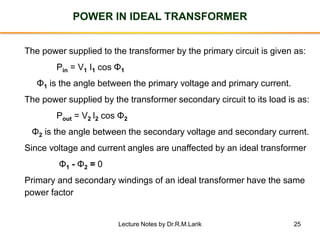
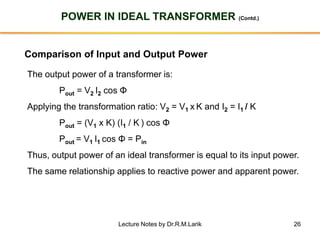
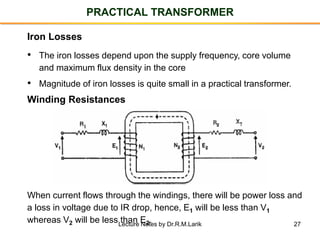
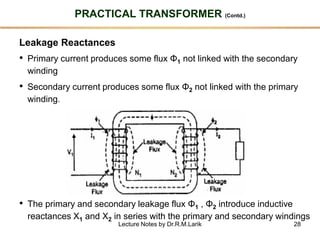
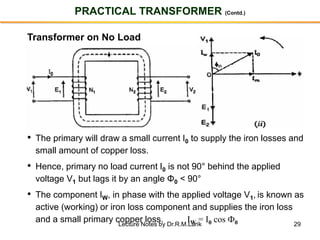
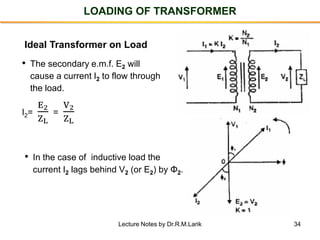
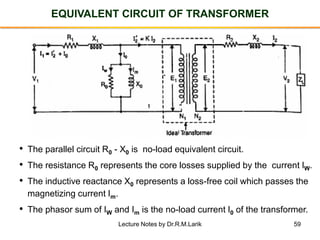
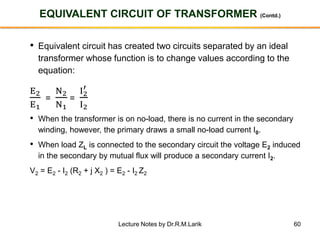
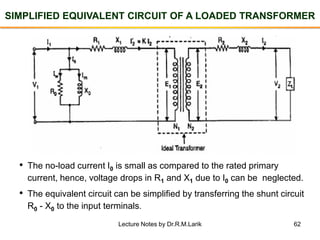
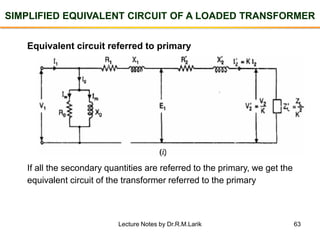
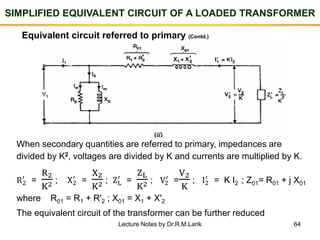
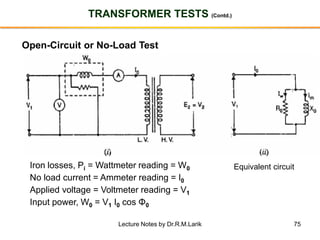
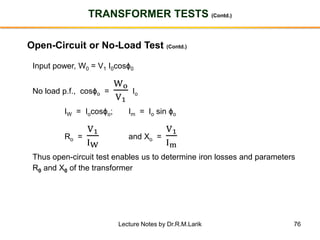
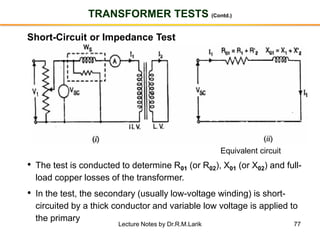
- A transformer essentially consists of two windings (primary and secondary) wound on a common laminated magnetic core. An alternating voltage applied to the primary induces an electromagnetic force in the secondary.
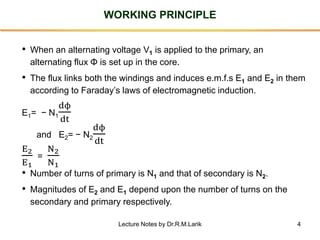
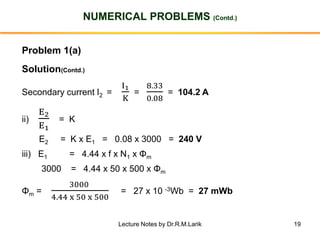
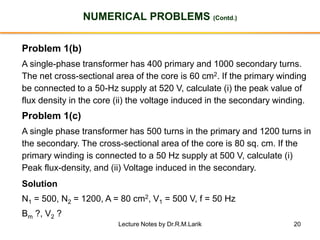
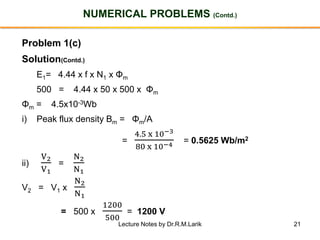
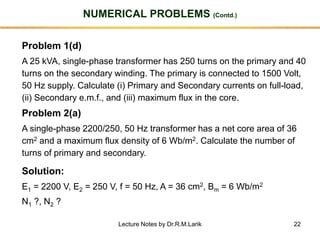
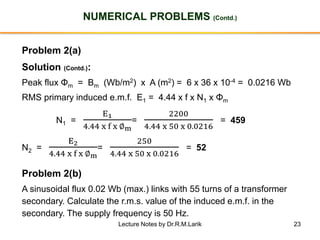
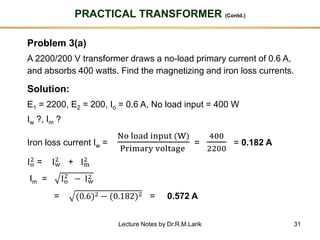
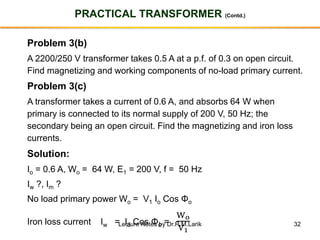
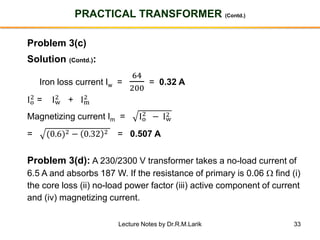
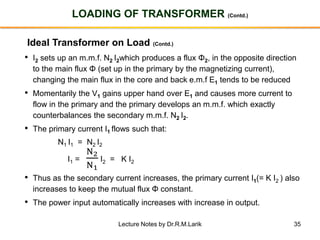
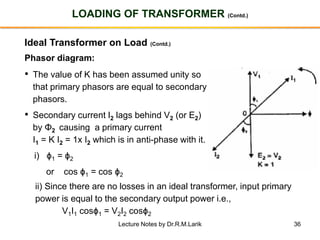
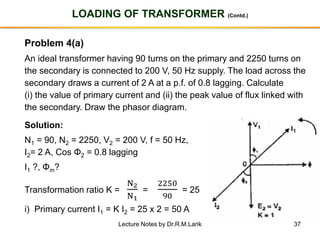
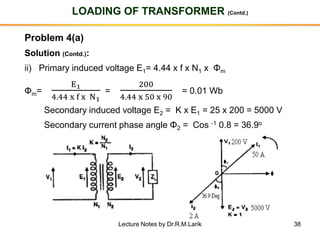
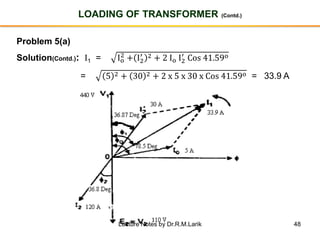
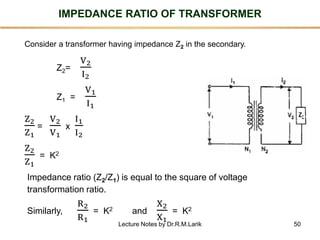
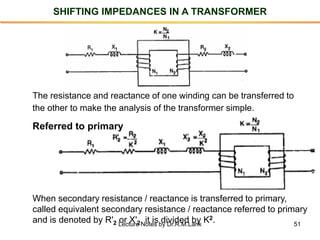
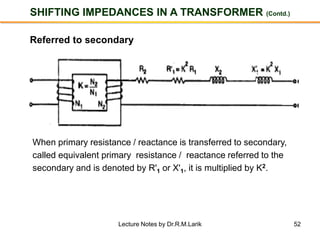
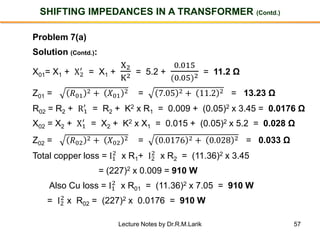
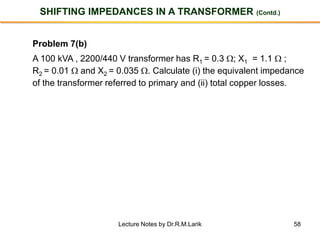
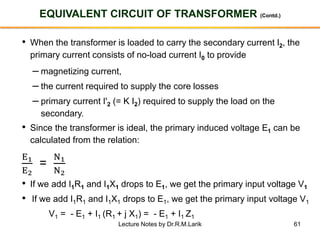
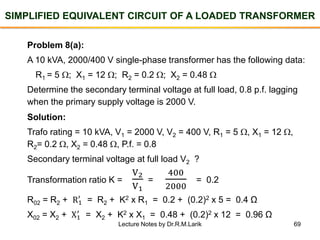
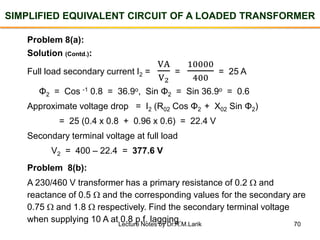
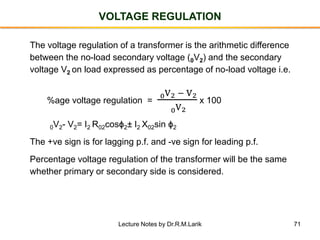
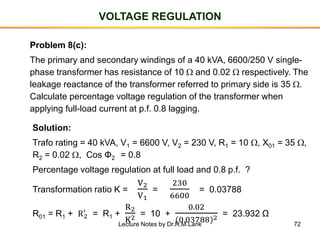
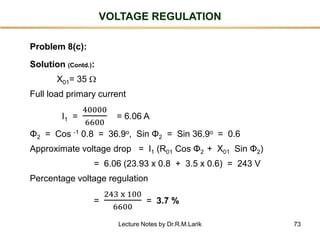
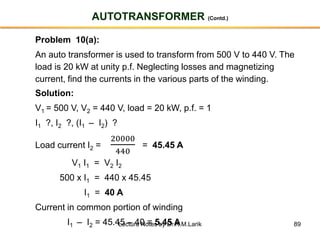
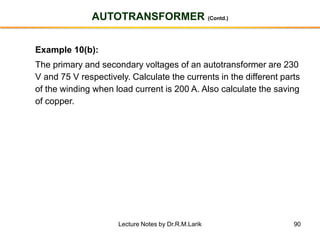
- The number of turns in each winding determines the ratio of voltages or currents between the primary and secondary. Calculations are provided for induced voltages, current transformations, and flux density based on transformer specifications.