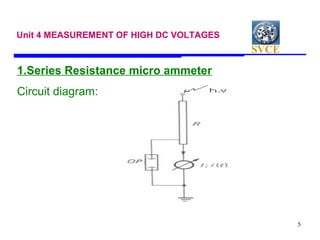
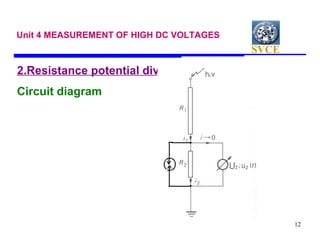
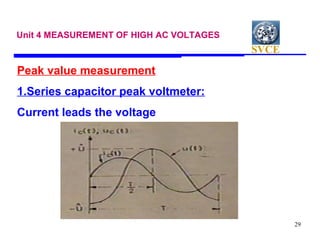
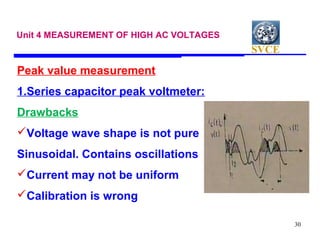
This document discusses various techniques for measuring high voltages, including DC, AC, and high frequency voltages. For DC voltages, it describes using a series resistance microammeter, resistance potential divider, and generating voltmeters. For AC voltages, it outlines series impedance voltmeters, potential transformers, electrostatic voltmeters, potential dividers, and sphere gaps. It provides details on measuring peak voltages using series capacitor peak voltmeters and using a peak voltmeter with a potential divider. It also discusses measuring RMS voltages with a peak voltmeter or electrostatic voltmeter.