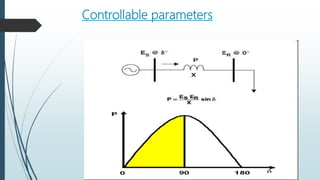
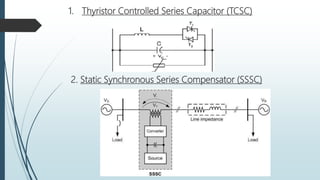
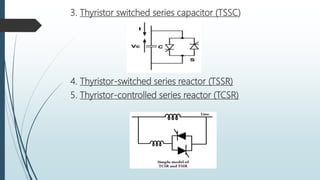
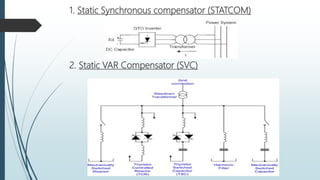
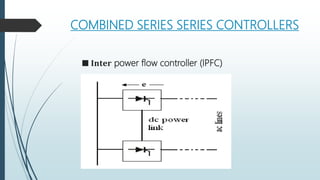
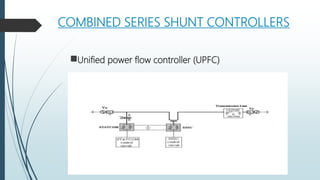
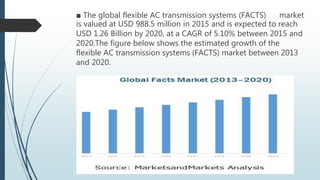
The document discusses the Flexible AC Transmission System (FACTS), which enhances the controllability and power transfer capacity of AC transmission systems through power electronics. It outlines the objectives, types, benefits, and disadvantages of FACTS controllers, highlighting various power electronic devices used and recent projects related to FACTS technology. The conclusion emphasizes the potential for wide-scale installation of FACTS devices by electrical utilities to improve power flow management.