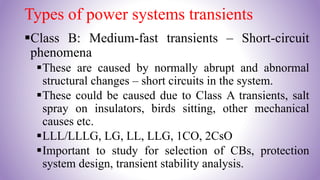
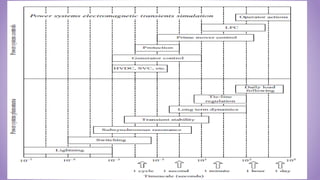
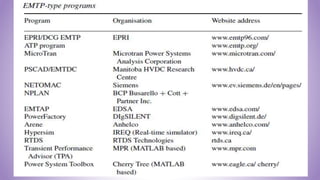
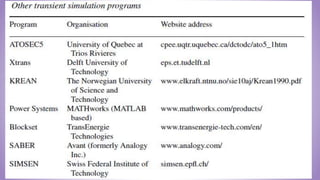
This document provides an introduction to power system transients. It discusses the sources of transients, both internal like capacitor switching and external like lightning. It classifies transients into three categories based on speed: ultrafast surges, medium-fast short-circuit phenomena, and slow transient stability issues. The effects of transients are outlined, such as damage to insulation, semiconductors, and contacts. The importance of studying transients for insulation design is emphasized to prevent breakdown under overvoltage conditions.