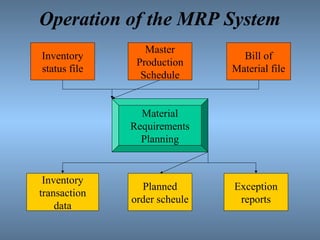
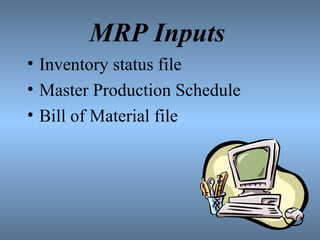
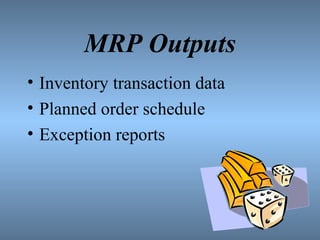
MRP is a computerized production planning and inventory control system that schedules component items as needed. It uses a bill of materials, master production schedule, and inventory status to determine material requirements and generate a planned order schedule. The goal of MRP is to ensure the right parts are available at the right time for finished goods production. It provides benefits like reduced inventory levels and component shortages, improved production schedules and customer service.