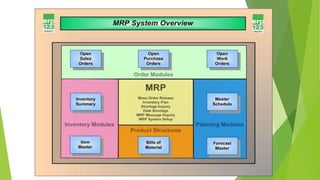
Material Requirements Planning (MRP) is a production planning and inventory control system used to manage manufacturing processes. MRP determines material requirements based on a master production schedule, bill of materials, and inventory status to ensure materials and components are available for production. The key objectives of MRP are to maintain minimum yet sufficient inventory levels and ensure the right materials are available at the right time for production. MRP provides benefits like improved scheduling, reduced inventory levels and costs, and better response to customer orders and market changes.