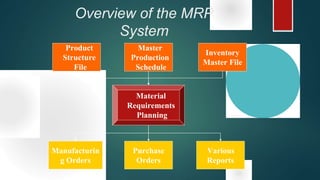
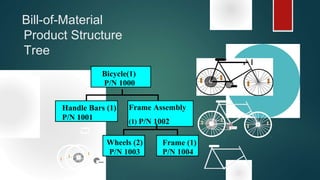
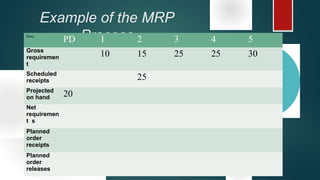
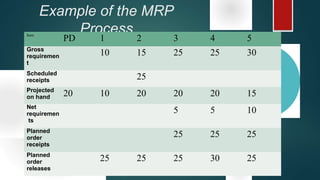
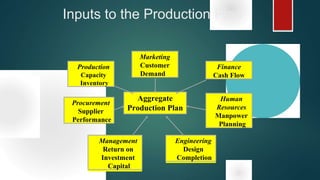
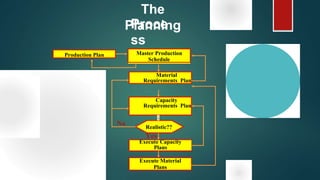
Material Requirement Planning (MRP) is a computerized inventory control and production planning system that helps manage and schedule manufacturing components based on order priorities and available capacities. It effectively reduces inventory levels, component shortages, and lead times while improving customer service and plant efficiency. The MRP process involves identifying requirements, running MRP to create suggestions, and firming those suggestions into manufacturing and purchasing orders.