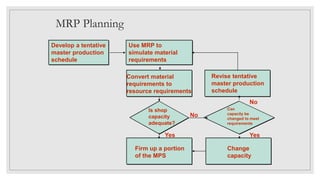
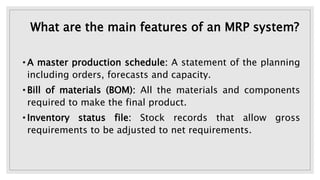
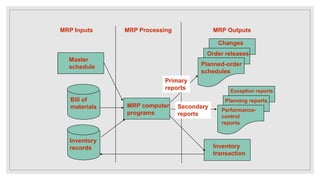
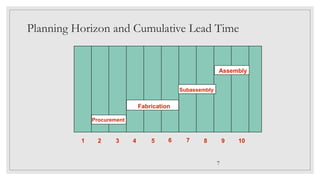
An MRP system is a planning tool that analyzes current inventory levels and production capacity to determine what goods need to be manufactured based on forecasts. It schedules production according to bills of materials to minimize inventory while meeting requirements within a fixed period. MRP works by exploding bills of materials to determine component requirements, netting requirements against stock levels, and offsetting to schedule production based on estimated lead times so items are available when needed. The system requires accurate input of master schedules, bills of materials, and inventory records to generate order releases and exception reports.