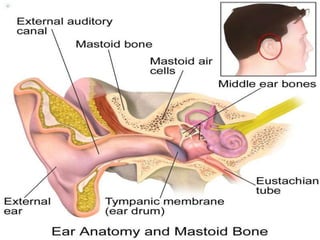
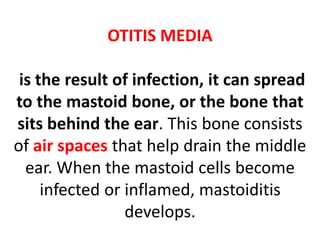
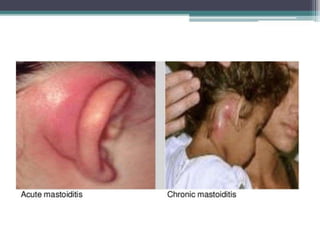
This document discusses mastoiditis, a bacterial infection of the mastoid air cells surrounding the inner and middle ear. It can develop as a result of an unresolved middle ear infection (otitis media) that spreads to the mastoid bone. Chronic suppurative otitis media and cholesteatoma are also discussed as potential causes of mastoiditis. The document covers etiological factors, management, and potential complications of mastoiditis such as facial paralysis, nausea/vomiting, and intracranial infections.