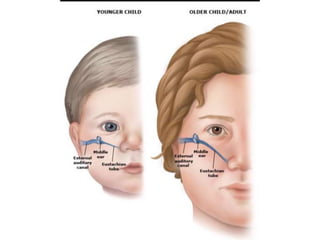
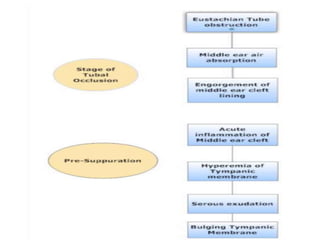
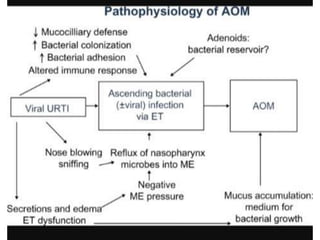
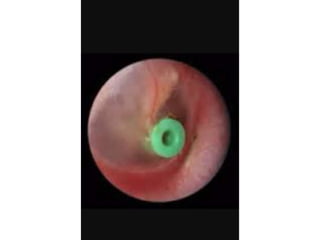
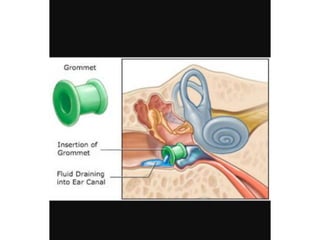
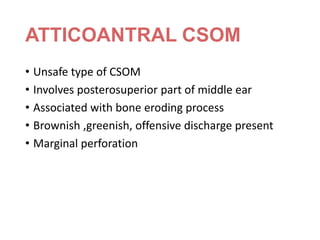
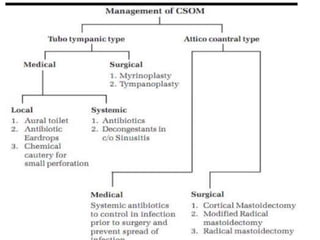
Otitis media refers to inflammation of the middle ear, most commonly seen in infants and children between 6 months and 2 years old. It can present as acute otitis media, otitis media with effusion, or chronic suppurative otitis media. Risk factors include young age, allergies, and infections like colds that can cause eustachian tube dysfunction. Treatment involves antibiotics, analgesics, myringotomy, or surgery depending on the type and severity. Proper management is needed to prevent complications and hearing loss.