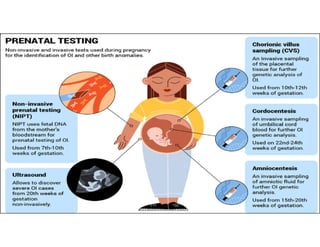
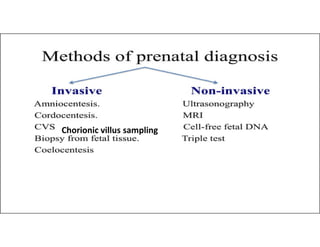
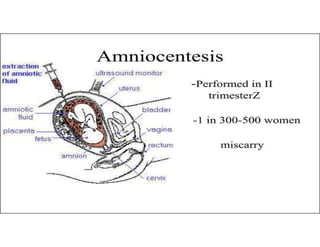
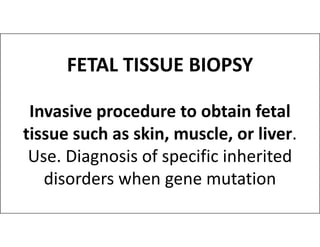
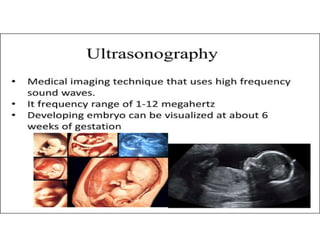
This document discusses advanced maternal age and the risks associated with pregnancy after age 35. It notes that while most women over 35 have healthy pregnancies, the risks of complications like preeclampsia, premature birth, and genetic disorders increase with age. Specifically, the risk of Down syndrome rises with maternal age. The document also outlines various prenatal tests that can assess the health of the fetus and screen for potential issues.