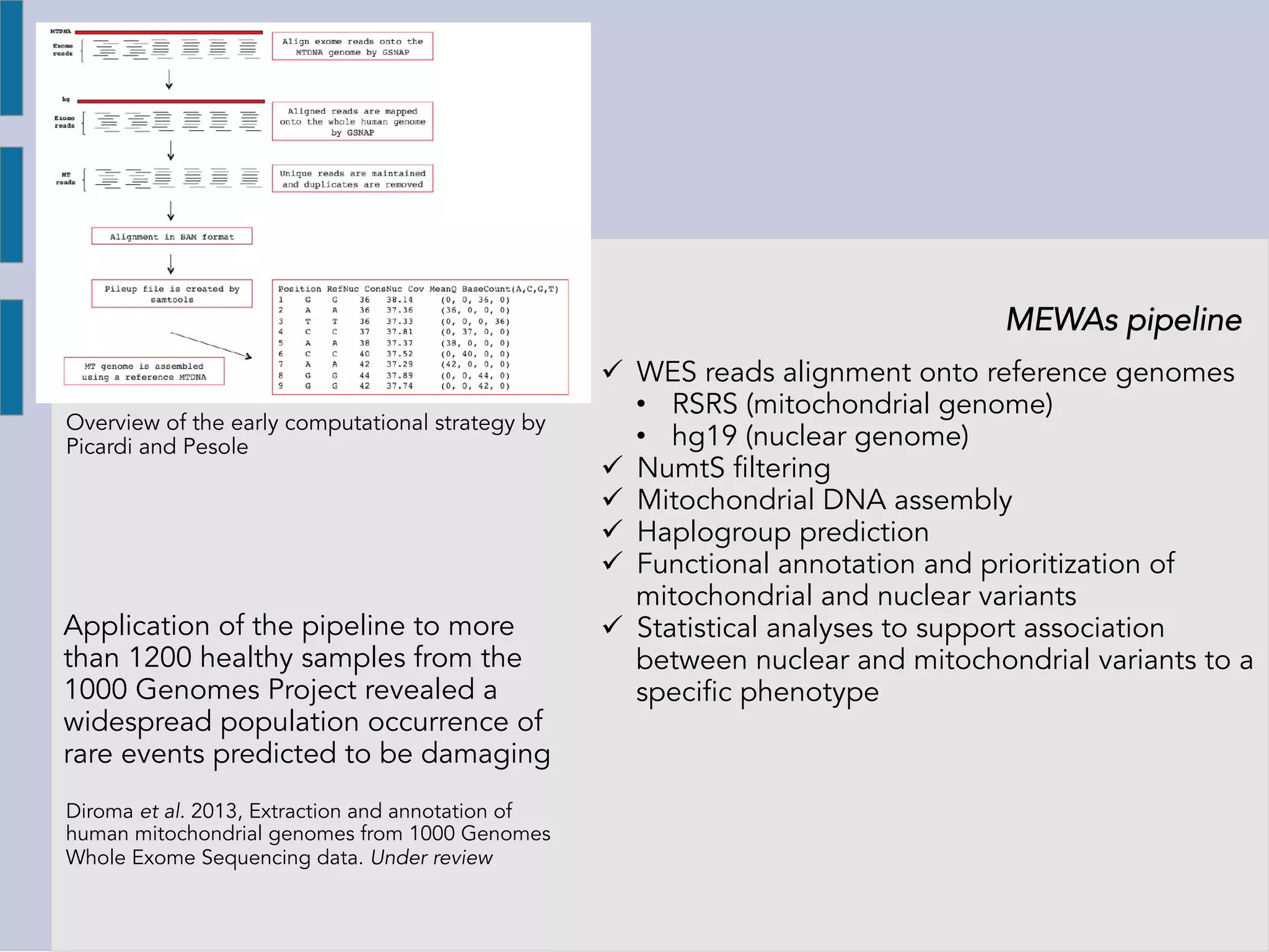
The document details the development of a bioinformatics system called Mitochondriome-Exome Wide Associations (MEWAS) for studying the relationships between mitochondrial DNA and nuclear exomes in physiological and pathological phenotypes. It discusses the importance of mitochondria in cellular functions, the impact of mitochondrial DNA mutations on various diseases, and the integration of mitochondrial and nuclear genomic data for research. Additionally, it outlines the computational strategies used in MEWAS to analyze data from the 1000 Genomes Project and highlights contributions from various academic professionals.