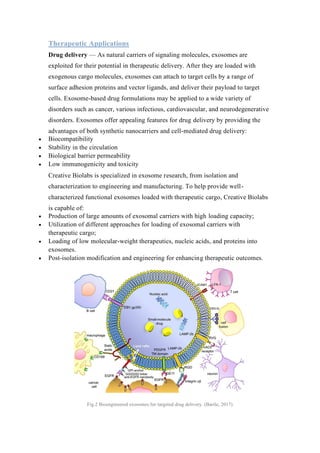
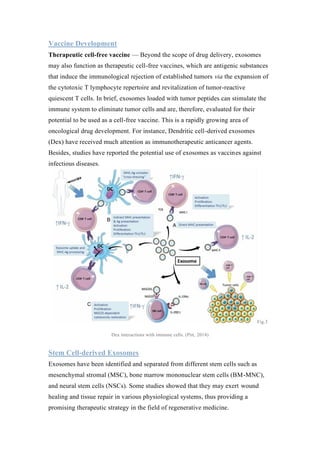
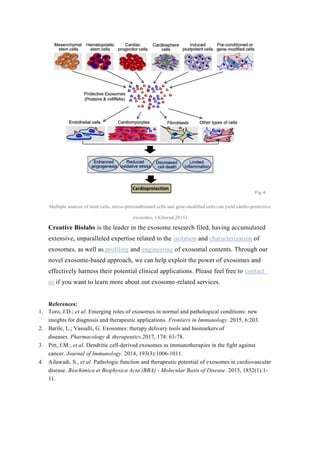
Exosomes have specialized functions and play key roles in physiological and pathological processes. As a result, exosomes show potential for clinical applications in prognosis, diagnosis, drug delivery, and vaccine development. Exosomes can serve as diagnostic biomarkers found in bodily fluids and allow for minimally invasive approaches. They also show promise as drug delivery vehicles due to their biocompatibility, stability, and low toxicity. Additionally, exosomes may function as therapeutic cell-free vaccines by stimulating immune responses against tumors or infections. Stem cell derived exosomes also demonstrate potential in regenerative medicine applications.