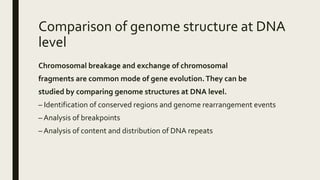
Comparative genomics involves analyzing and comparing the genomes of different organisms to understand evolution, gene function, and disease. Genomes can be compared at multiple levels, including overall structure, coding regions, and non-coding regions. Comparing gene location, structure, characteristics, and sequence similarity provides insights into how genomes have changed over time and what distinguishes species. Comparative genomics also aids in drug discovery by identifying potential drug targets and furthering our understanding of pathogenesis. The field has wide-ranging impacts on biology, agriculture, medicine, and conservation efforts.