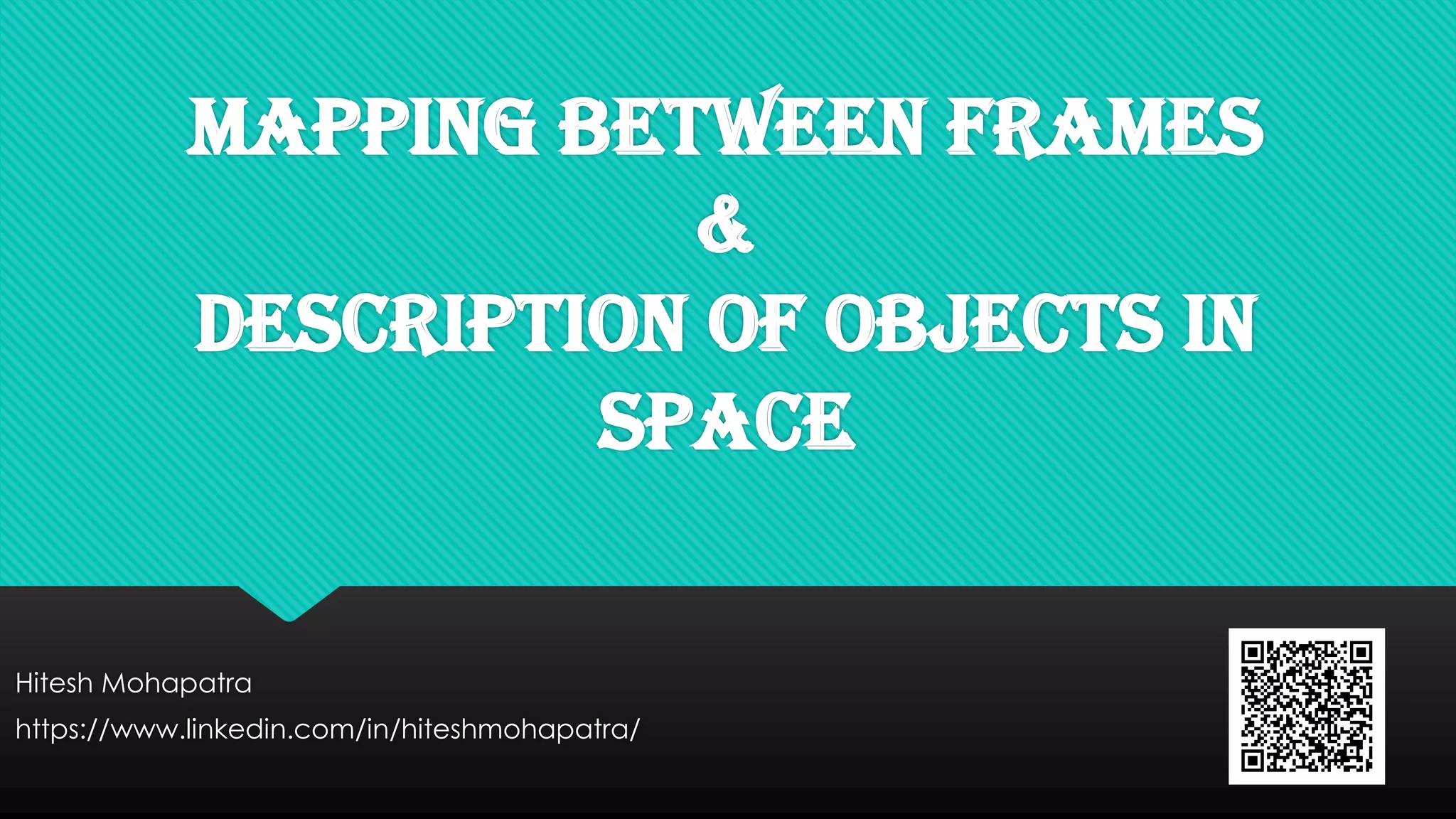
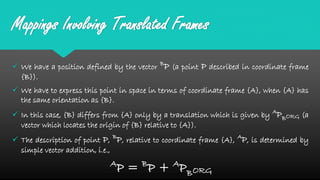
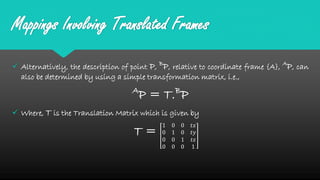
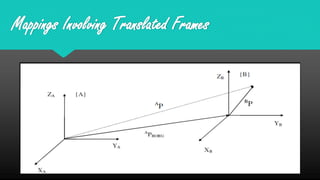
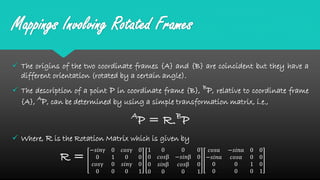
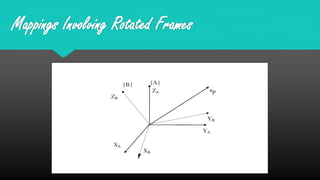
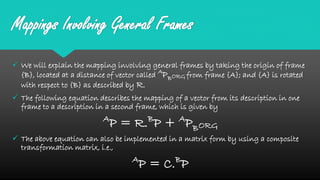
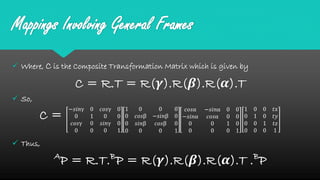
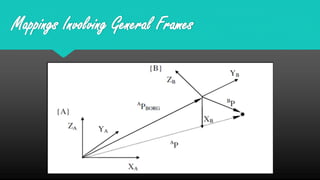
Mapping between frames refers to changing the description of a point or vector from one coordinate frame to another. There are three possibilities for how the second frame relates to the first: rotated, translated, or both rotated and translated. Translations involve moving the origin of one frame relative to the other while keeping the axes parallel. Rotations involve changing the orientation of one frame relative to the other while keeping the origins coincident. A general mapping involves both a rotation and a translation, which can be represented by a composite transformation matrix that performs the rotation followed by the translation. Homogeneous transformation matrices are also used to describe both the position and orientation of frames in space.