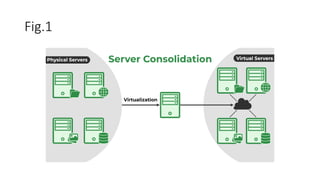
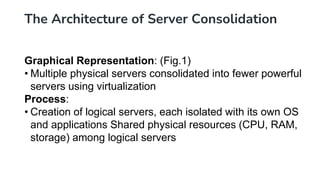
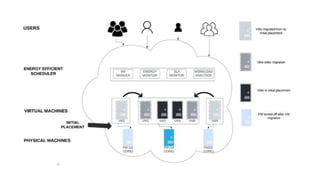
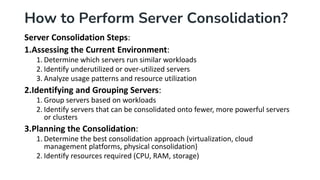
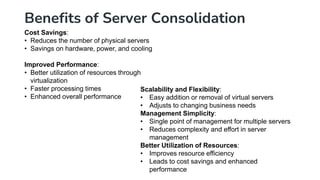
Server consolidation in cloud computing involves combining multiple servers into a more powerful server or cluster to enhance efficiency and reduce costs. This process utilizes virtualization technology, allowing several virtual servers to operate on a single physical server, thus improving resource utilization, scalability, and management simplicity. The steps for consolidation include assessing the current environment, grouping servers based on workloads, planning the consolidation approach, and ongoing monitoring for optimal performance.