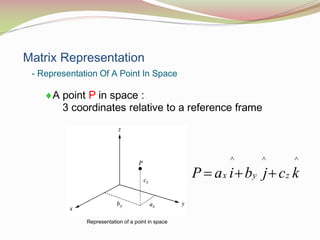
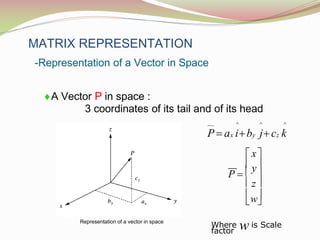
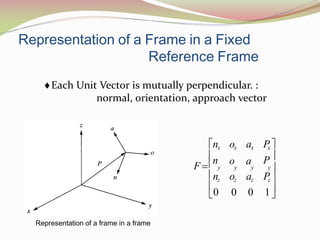
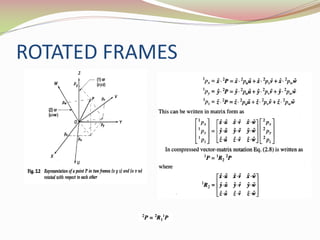
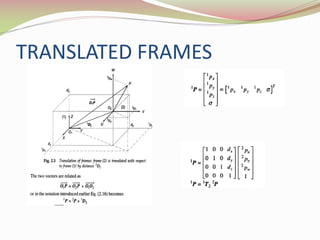
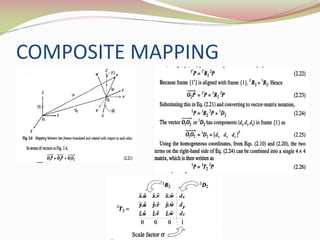
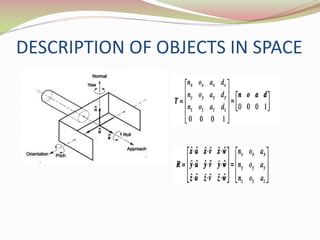
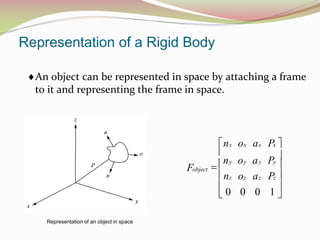
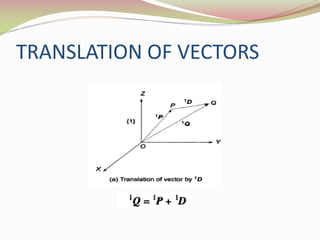
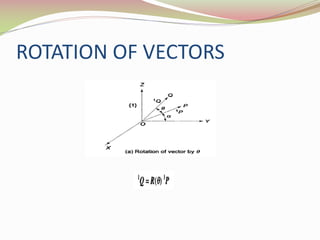
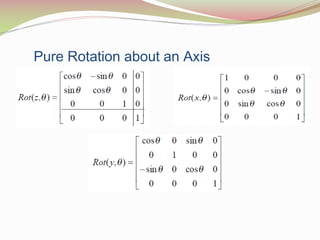
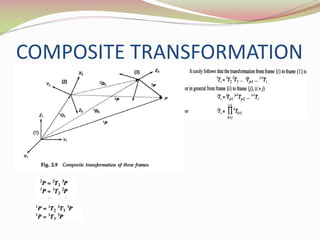
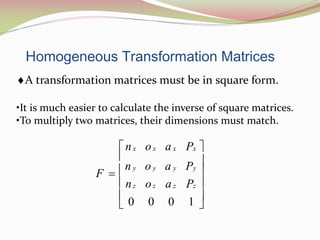
This document discusses the transformation of vectors with respect to objects in 3D space. It introduces vectors and objects, and how they can be represented using matrices and frames. It then covers how to map vectors between rotated frames, translated frames, and through composite mappings using homogeneous transformation matrices. The key concepts are representing points and vectors in space with matrices, using frames to describe objects, and transforming vectors between frames through rotation, translation, and composite transformations.