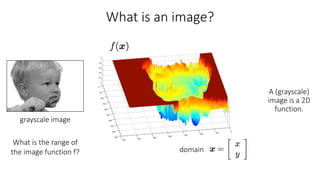
This document summarizes key points from a lecture on 2D image transformations:
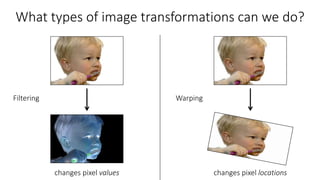
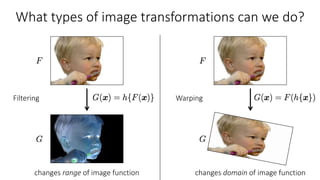
- 2D image transformations can be classified as either changing pixel values (filtering) or changing pixel locations (warping).
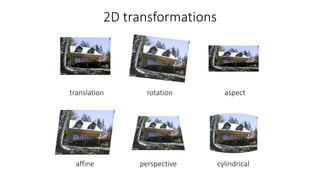
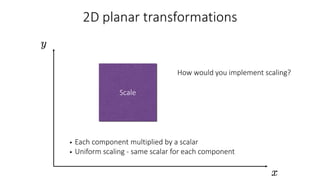
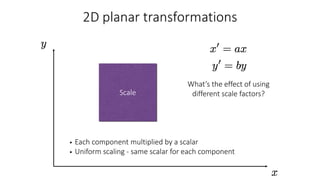
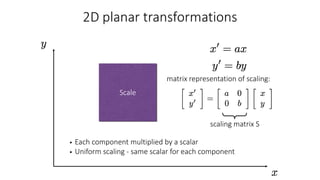
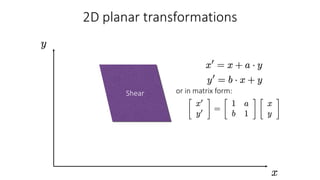
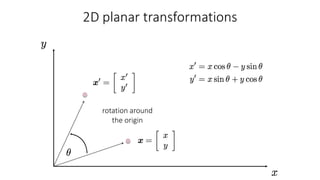
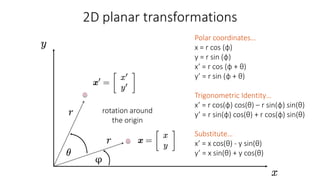
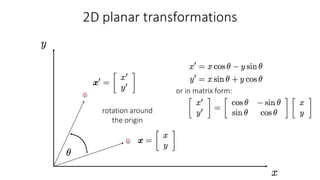
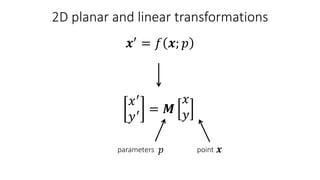
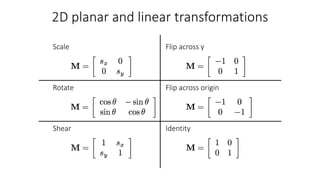
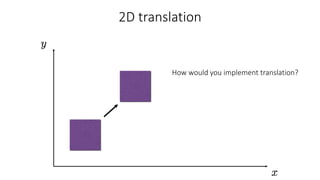
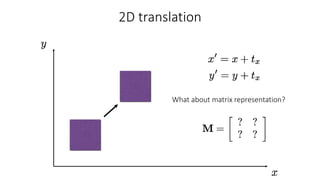
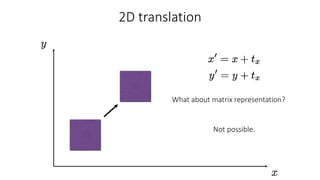
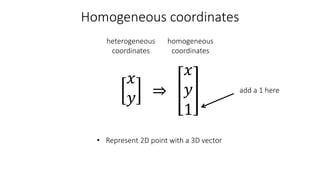
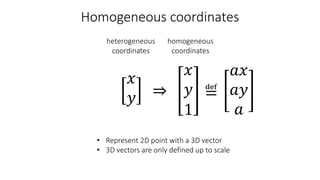
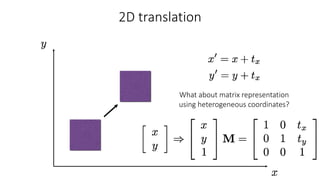
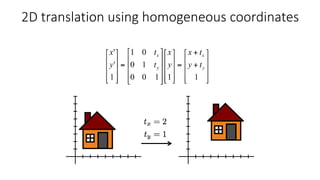
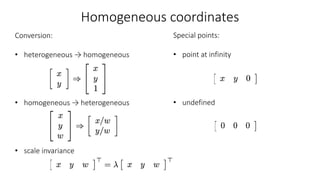
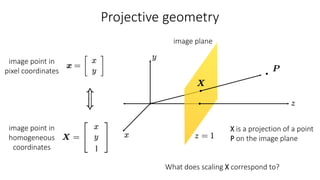
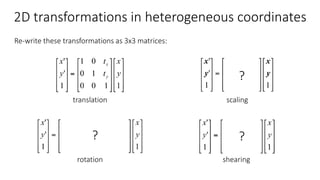
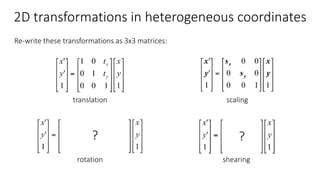
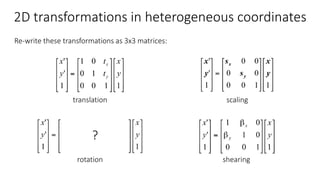
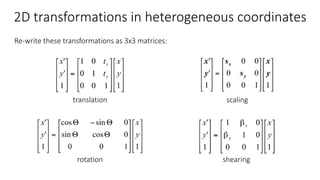
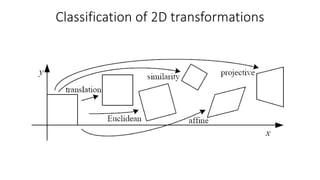
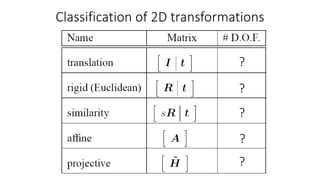
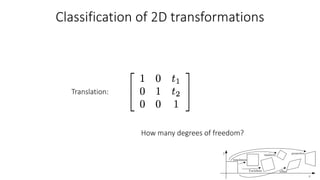
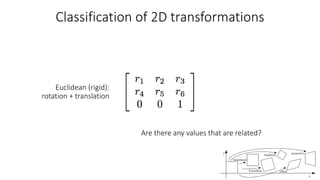
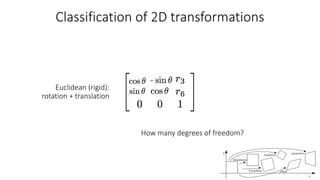
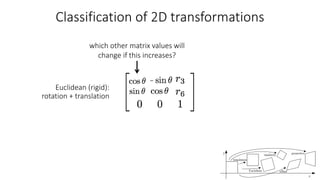
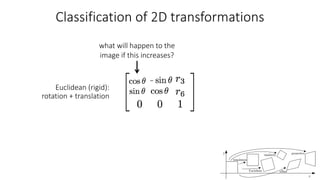
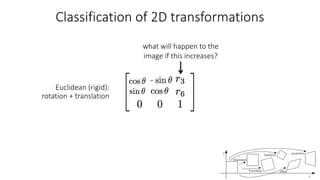
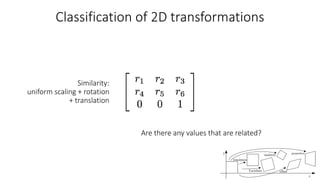
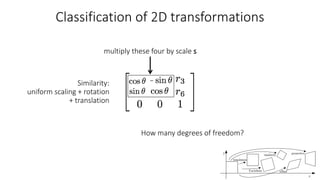
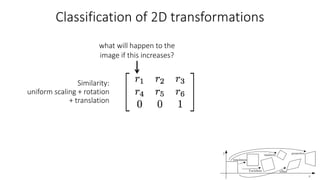
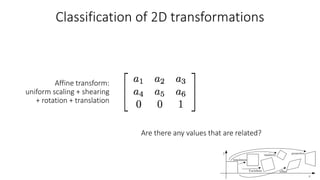
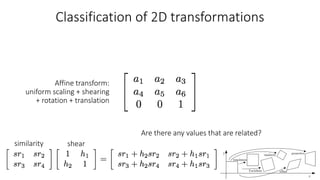
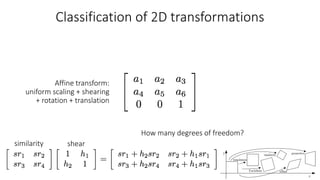
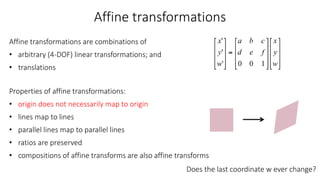
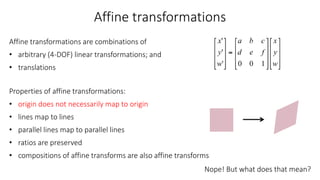
- Common 2D transformations discussed include translation, rotation, scaling, shearing, and affine transformations. Matrix representations of these transformations using homogeneous coordinates were presented.
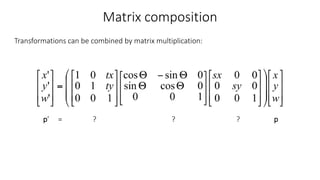
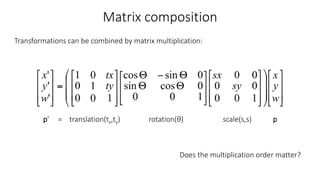
- Transformations can be combined through matrix multiplication. The order of multiplication matters.
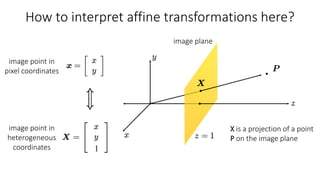
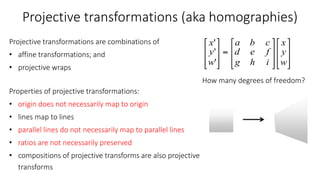
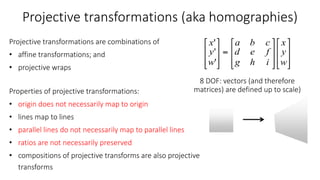
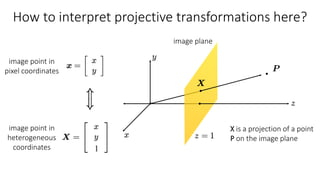
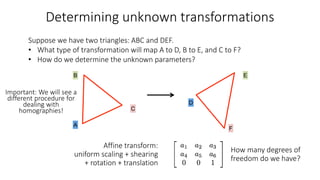
- Transformations were classified based on degrees of freedom, with affine transformations having 6 degrees and projective transformations having 8 degrees of freedom.
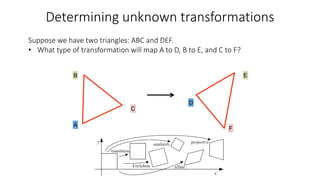
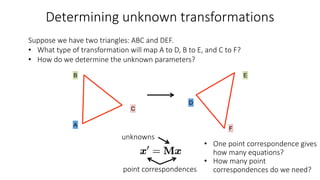
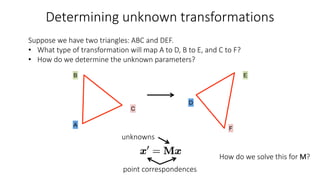
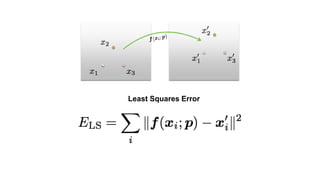
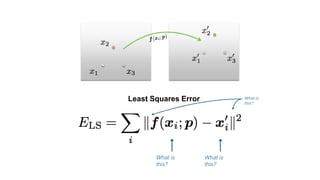
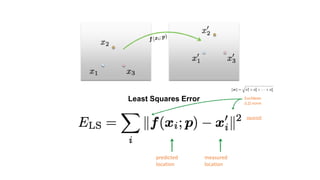
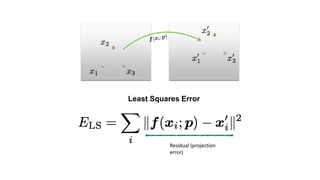
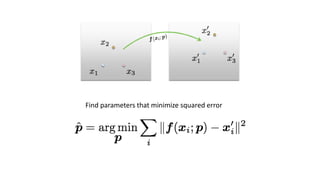
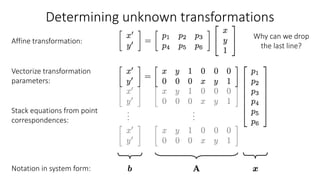
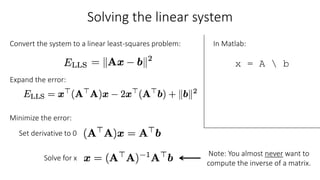
- Determining unknown affine transformations from point correspondences between images was discussed. At least 3 point correspondences are needed