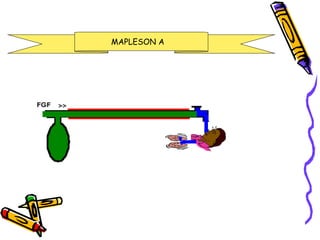
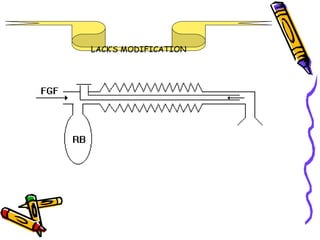
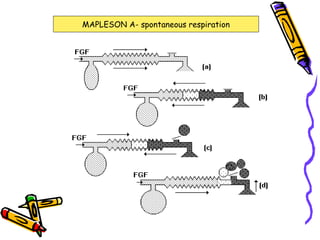
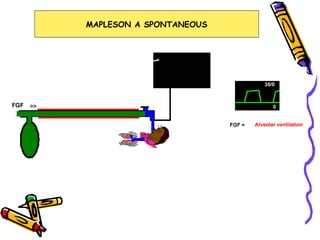
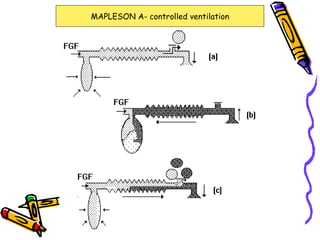
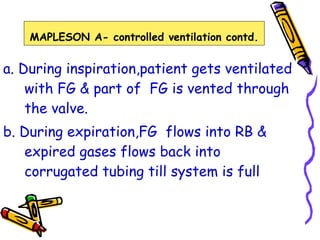
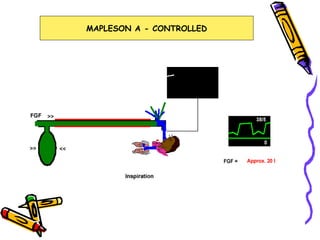
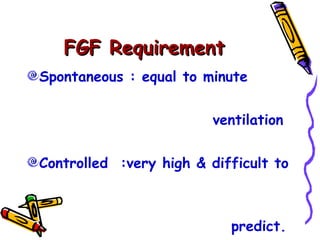
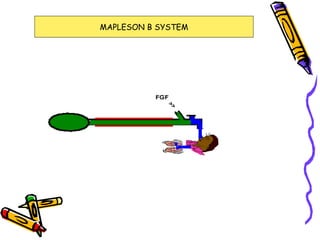
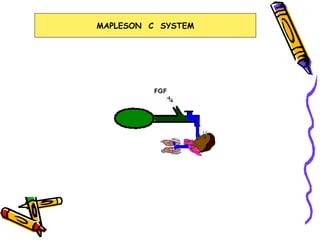
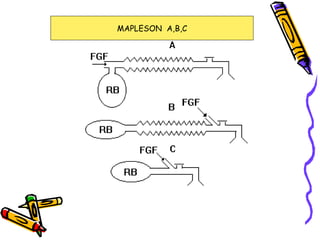
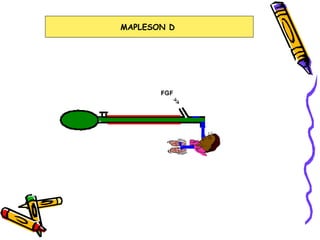
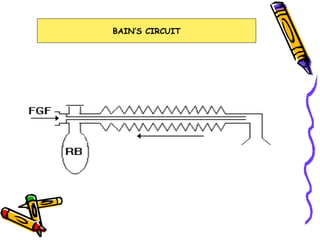
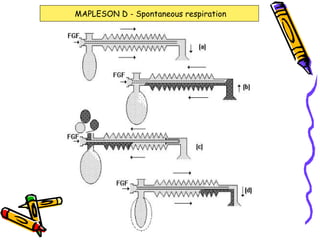
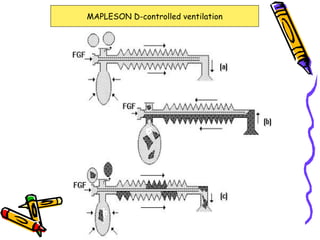
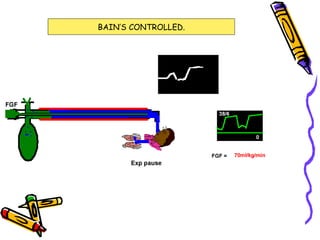
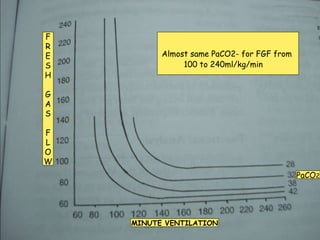
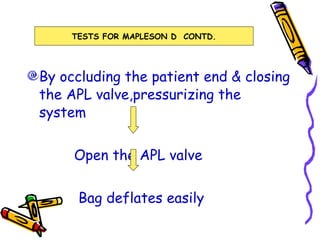
There are several types of Mapleson breathing systems classified based on the position of the reservoir bag. Mapleson A has an afferent reservoir with the bag attached to the fresh gas inlet. Mapleson D has an efferent reservoir with the bag attached to the patient outlet. Both systems allow for spontaneous or controlled ventilation but Mapleson D is more efficient due to continuous mixing of fresh gas and exhaled gases. The systems are tested for leaks and proper functioning using various occlusion and pressurization techniques.