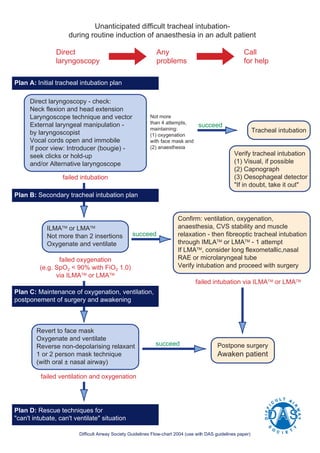
1. The document outlines a 4 plan approach for managing difficult or failed tracheal intubation during anesthesia induction.
2. Plan A involves initial direct laryngoscopy and use of introducers or alternative laryngoscopes if poor view is obtained.
3. Plan B involves use of supraglottic airway devices like ILMA or LMA if Plan A fails, with fiberoptic intubation through the device.
4. Plan C maintains oxygenation and ventilation by reverting to a face mask if intubation fails via Plan B, postponing surgery and awakening the patient.
5. Plan D involves rescue techniques if ventilation and oxygenation cannot be maintained as