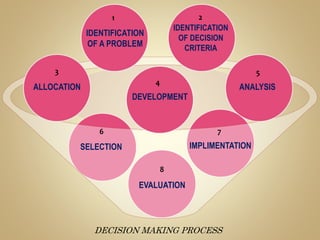
The document outlines the decision-making process, which involves identifying problems and opportunities, evaluating alternatives, and implementing solutions. Key steps include identifying the problem, setting criteria, developing and analyzing alternatives, selecting the best option, implementing the decision, and evaluating the outcomes. Effective decision-making is crucial for resource utilization, business growth, and employee motivation amidst uncertainty and conflicting viewpoints.