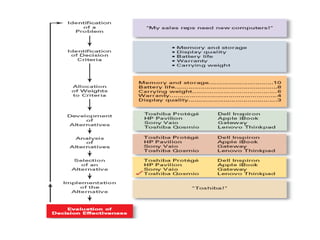
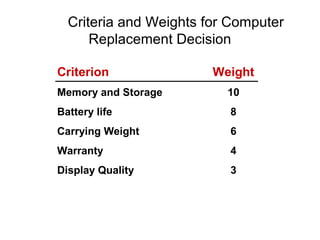
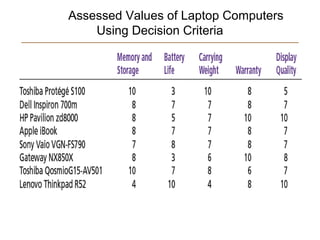
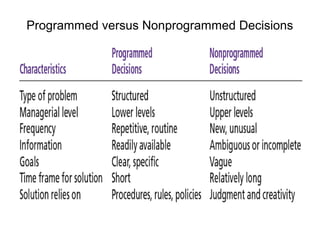
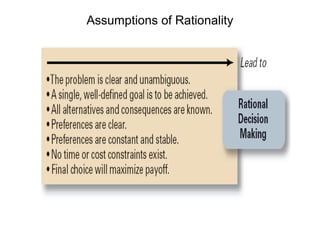
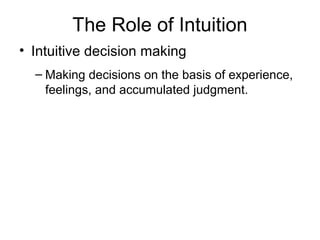
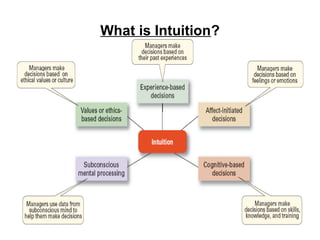
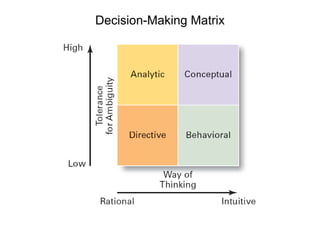
The document discusses the key steps in the decision making process: [1] identifying the problem and criteria for evaluating alternatives, [2] developing and analyzing potential alternatives, and [3] selecting, implementing, and evaluating the alternative chosen to resolve the problem. It covers identifying structured vs. unstructured problems, programmed vs. non-programmed decisions, and models of rational vs. intuitive decision making. The document also discusses different decision making styles and criteria that may be weighted to analyze alternatives.