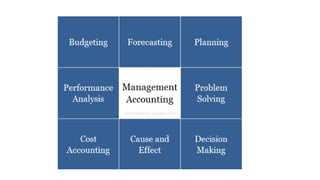
The document provides an introduction to management accounting, outlining its principles, definitions, objectives, and features. It covers essential topics such as financial statements, ratio analysis, leverage analysis, and fund flow and cash flow statements, emphasizing the role of management accounting in aiding decision-making. The scope and functions of management accounting are also discussed, illustrating its importance in financial planning and control within an organization.