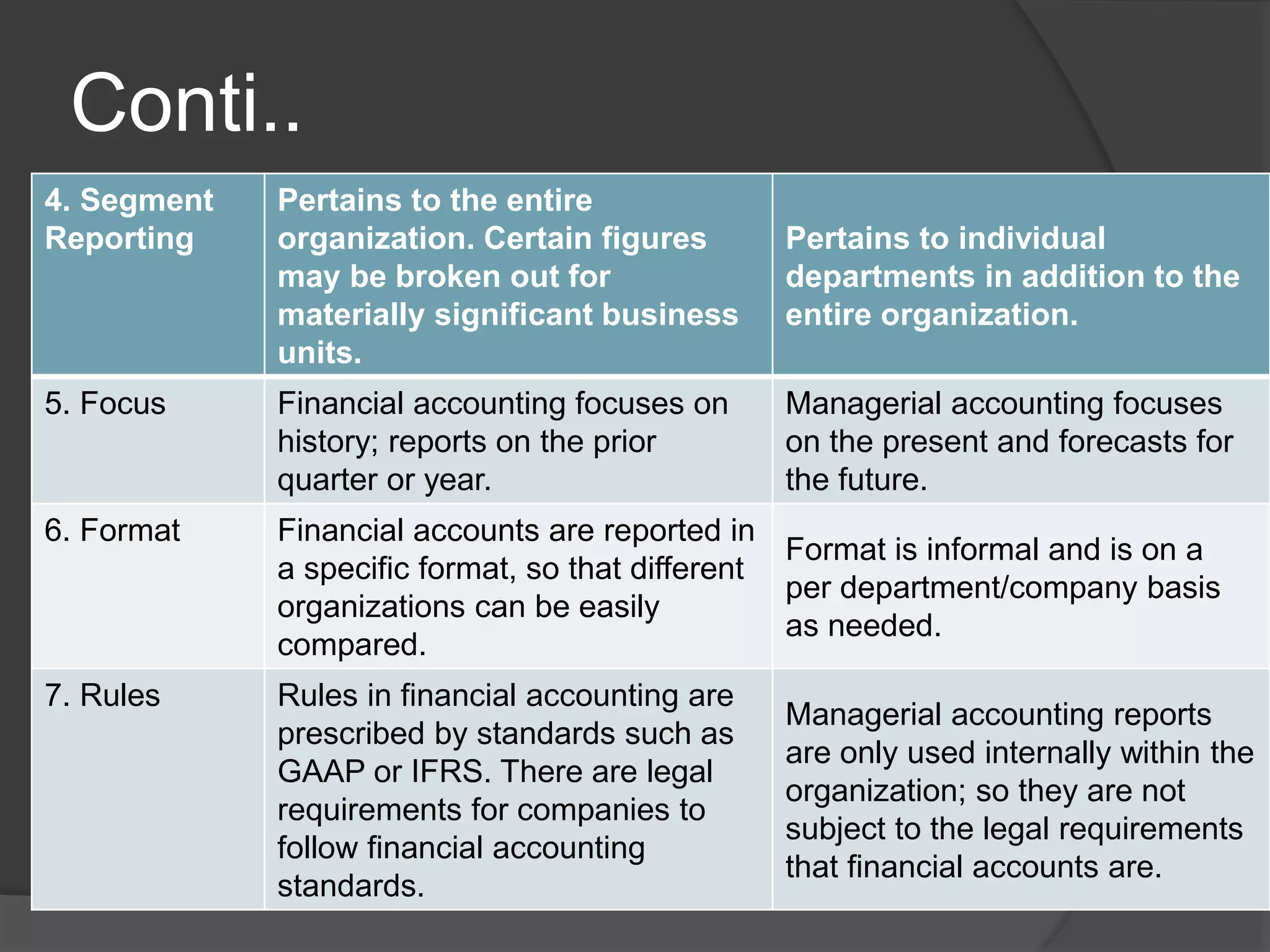
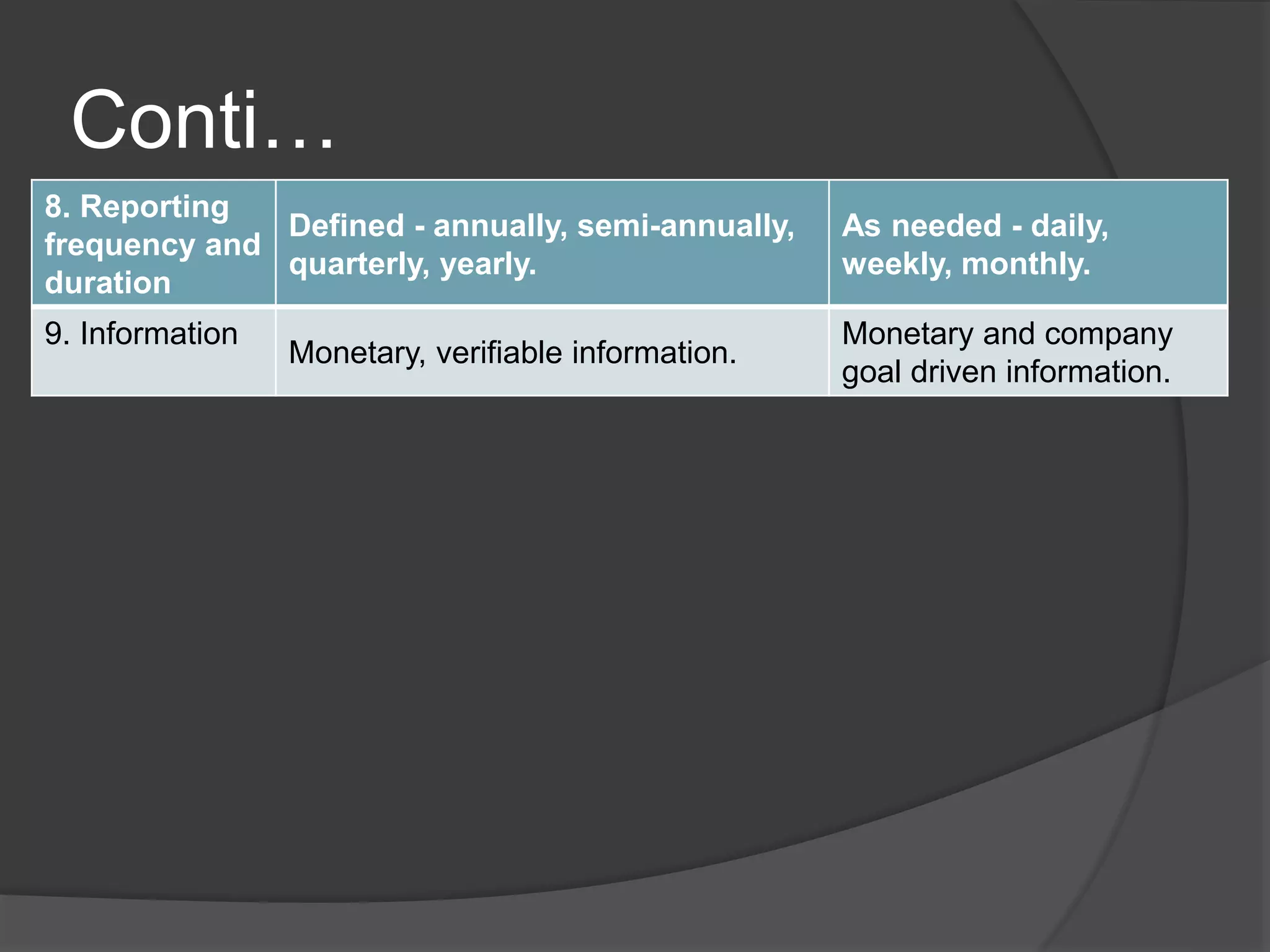
Management accounting provides internal accounting information to assist management in planning, decision-making, and controlling operations. It identifies, measures, analyzes, interprets, and communicates financial and non-financial information to help the organization achieve its goals. Management accounting focuses on the future and is aimed at helping managers make decisions, while financial accounting provides external reporting focused on the past to parties outside the organization like shareholders and regulators.