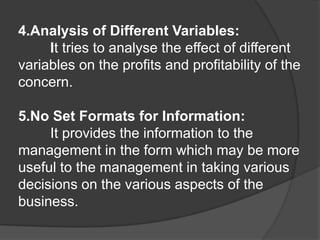
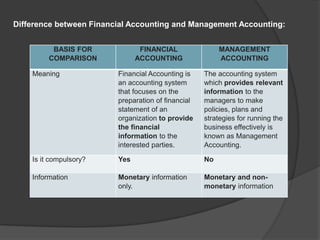
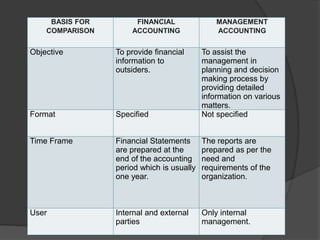
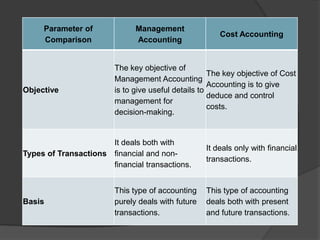
This document discusses management accounting. It defines management accounting as using accounting data to assist management with policymaking, planning, control, and decision-making. The objectives of management accounting include better planning, promoting efficiency, budget preparation, analyzing transactions, and interpreting financial statements. Management accounting is selective in the data it presents, provides data but not decisions, is concerned with the future, and analyzes different variables without set formats. Its merits include measuring performance versus budgets and improving efficiency and relations. Its limitations include relying on other accounting areas and requiring knowledgeable management and large organizations.