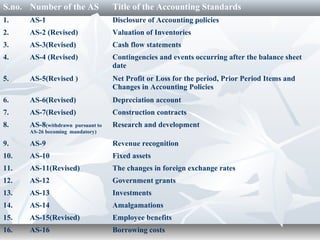
Accounting standards are written policies that provide guidance on recognizing, measuring, presenting, and disclosing accounting transactions and events. They aim to standardize accounting policies and financial statement disclosures to improve reliability and comparability. India has 32 accounting standards issued by ICAI that are largely based on International Financial Reporting Standards and cover topics like revenue recognition, investments, employee benefits, and intangible assets.