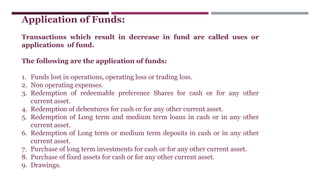
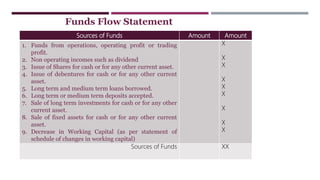
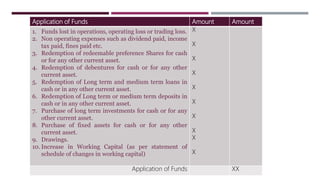
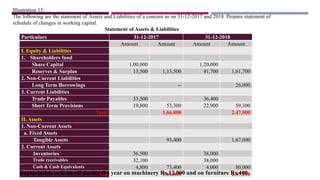
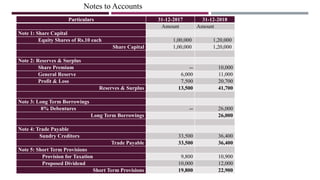
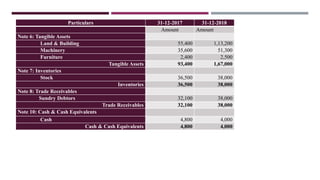
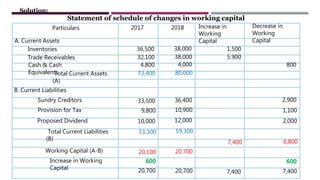
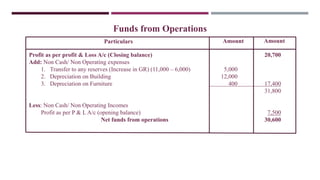
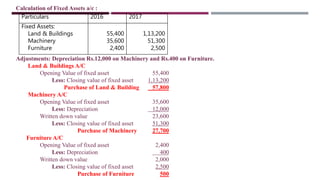
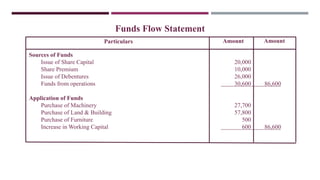
The document provides a comprehensive overview of management accounting, including definitions, principles, and various analytical techniques such as ratio analysis, fund flow statements, and cash flow statements. It discusses the relationship between management, accounting, and decision-making processes, highlighting the importance of financial information for internal management. Additionally, it outlines the sources and applications of funds in the context of financial analysis and control.