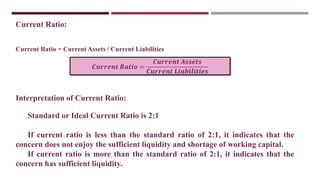
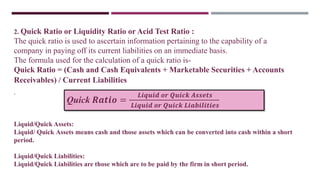
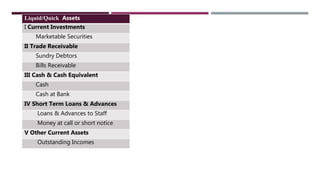
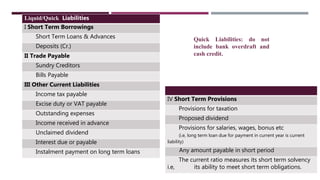
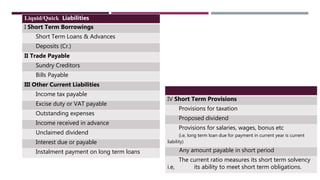
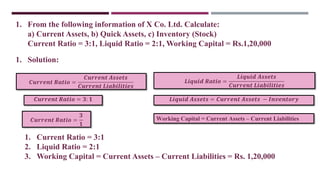
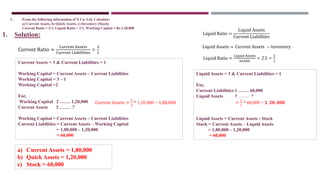
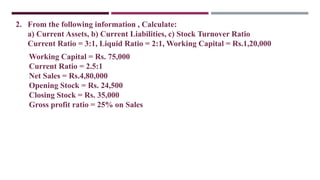
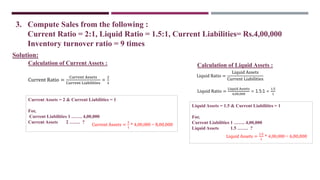
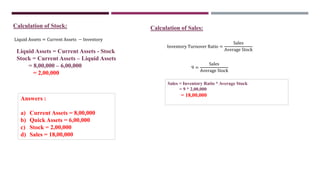
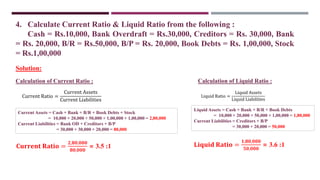
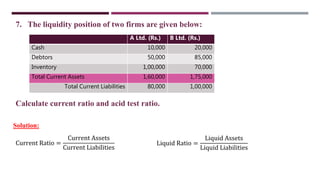
The document discusses management accounting ratio analysis, focusing on liquidity ratios which assess a company's ability to meet short-term obligations. It defines various financial ratios, including current, quick, cash, and stock to working capital ratios, explaining their calculations and interpretations. Additionally, the document provides examples and problems for calculating current assets, current liabilities, and other financial metrics.