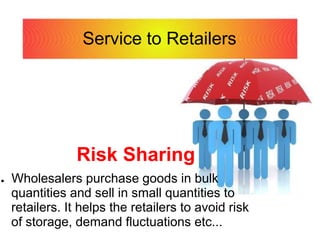
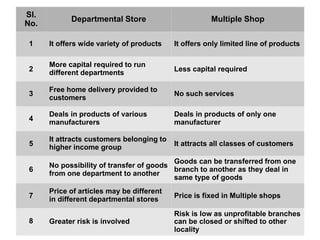
This document discusses different types of internal trade in India. It describes wholesale trade as buying and selling goods in large quantities from manufacturers to retailers. Wholesalers help facilitate large-scale production and provide storage, financing, and marketing support to manufacturers and credit and specialized knowledge to retailers. Retail trade involves the sale of goods to consumers. Retailers are either itinerant traders without fixed locations or operate out of fixed shops. Large retailers include department stores, chain stores, and consumer cooperative stores.























































![MULTIPLE SHOPS
[CHAIN SHOPS]
A Multiple shop is a large scale retail organisation with a number of
branches at different places under one ownership and management.
Head office controls the branches through Branch Managers. They
supply goods to the branches.
Eg : Bata shoe stores](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/internaltradenew-220912095354-a2236fa3/85/internal-trade-new-pptx-58-320.jpg)











![SUPER MARKET
[Super Bazaar / Self Service Store]
Super Market is a large scale retail store selling a wide
variety of consumer goods.
They deal in consumer products such as grocery,
utensils, electronic appliances etc...](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/internaltradenew-220912095354-a2236fa3/85/internal-trade-new-pptx-71-320.jpg)



