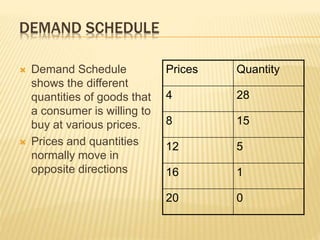
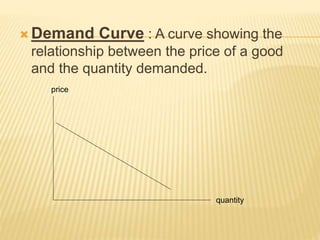
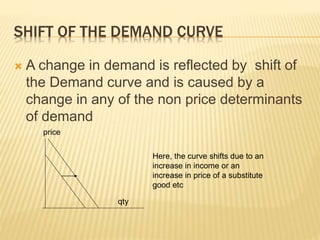
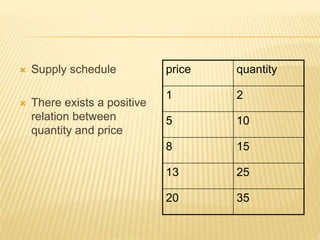
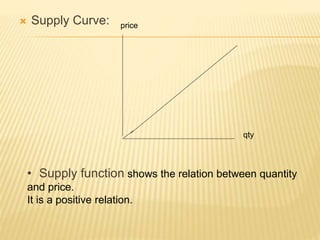
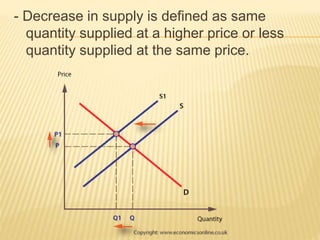
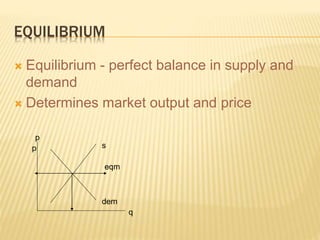
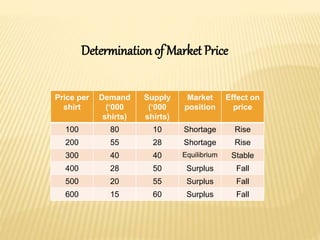
The document discusses different market structures including perfect competition, monopoly, monopolistic competition, oligopoly, and duopoly. Perfect competition is characterized by many small firms, homogeneous products, free entry and exit, and price-taking behavior. A monopoly has a single seller of a unique product in an industry with high barriers to entry. Monopolistic competition involves differentiated products that are close substitutes. Oligopoly describes an industry with a small number of large firms where the actions of one influence others. Duopoly is a specific type of oligopoly with only two firms controlling the market. Examples of each market structure are provided.