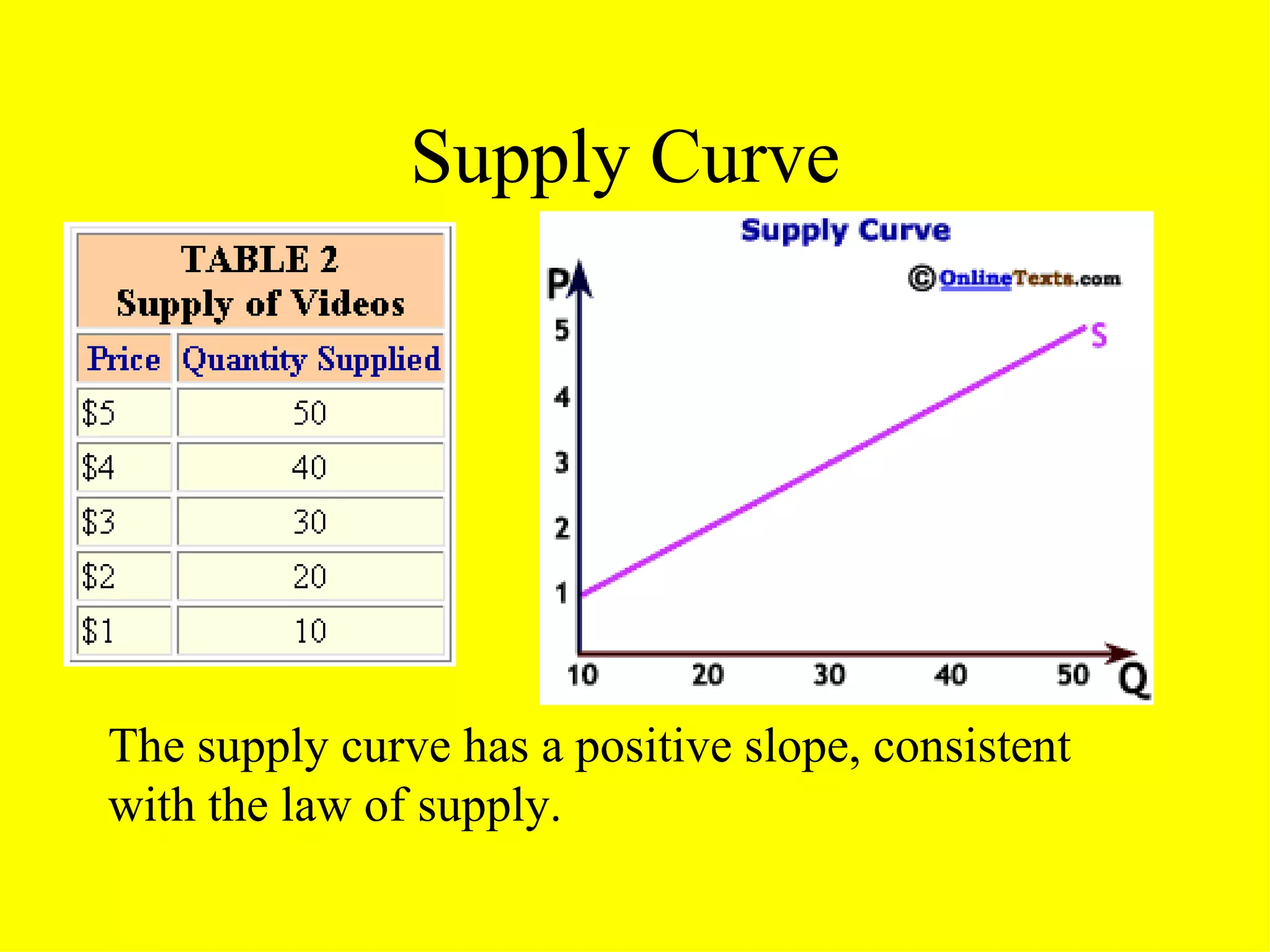
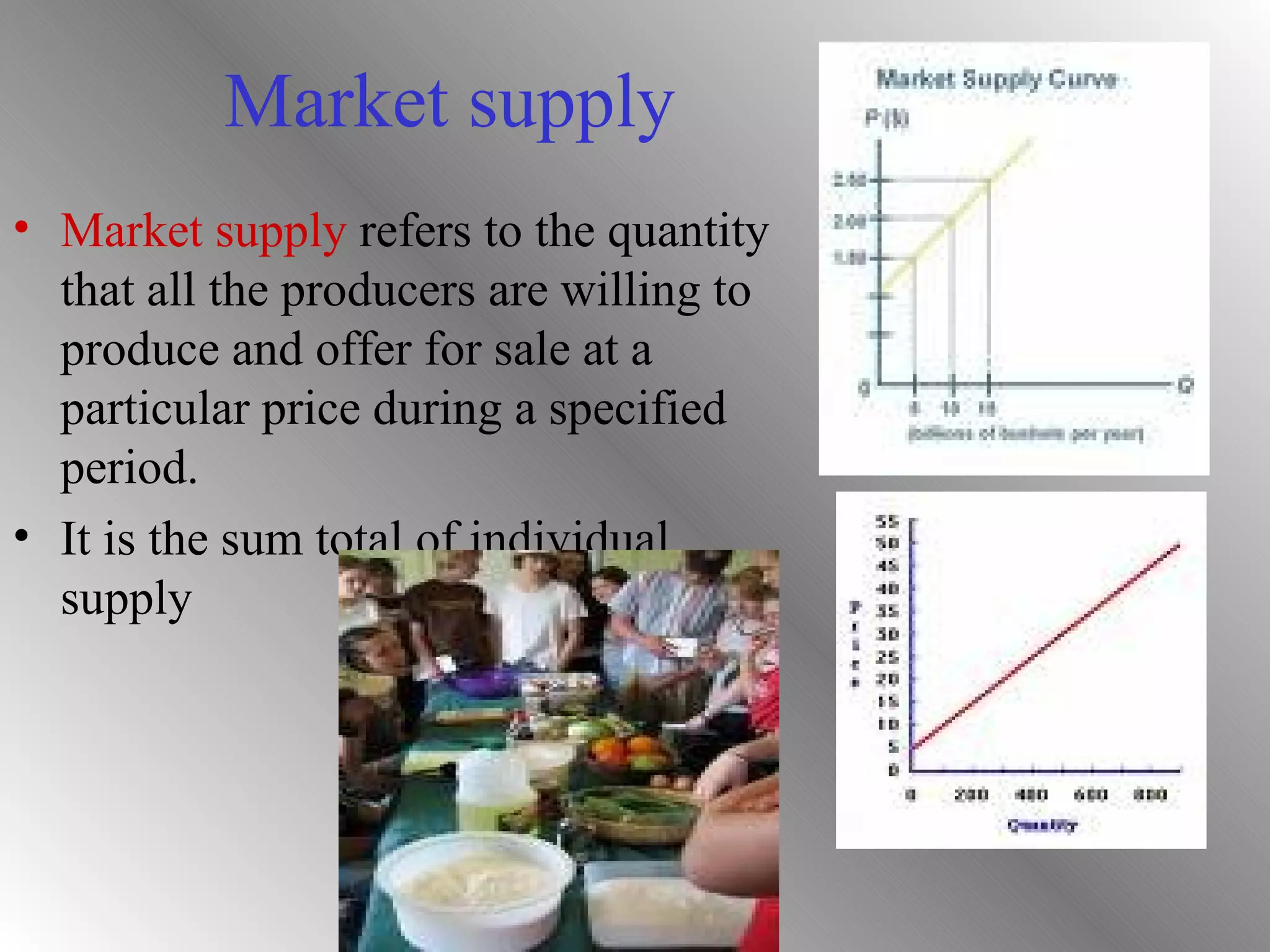
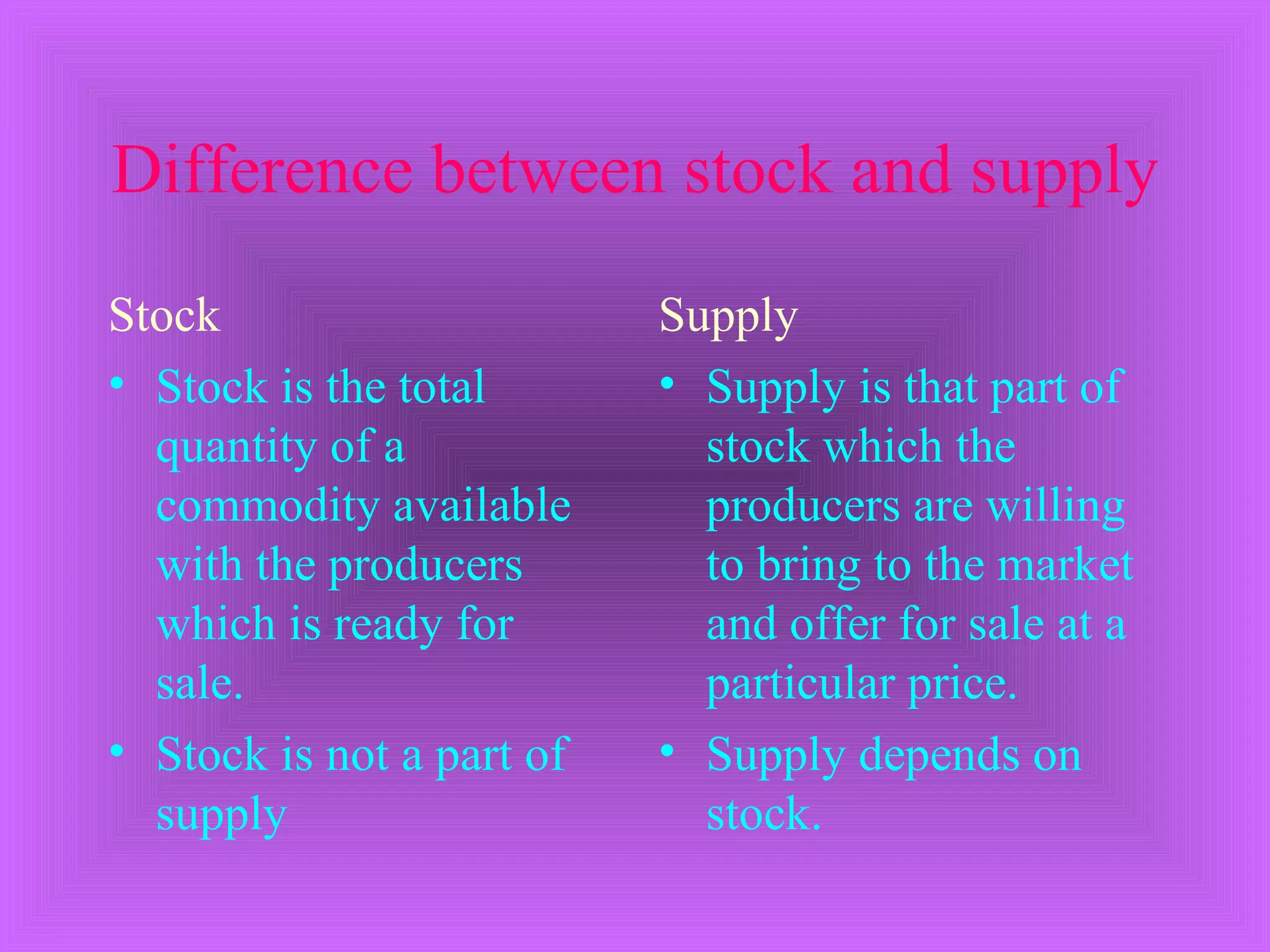
Supply refers to the quantity of a commodity that producers are willing and able to sell at a given price in a market during a specific time period. The three key aspects of supply are that it is a quantity, it is determined by price, and it is a flow rather than stock variable. Individual supply is the quantity a single firm is willing to produce, while market supply is the total quantity from all producers. Supply is positively impacted by higher prices and negatively impacted by higher input costs and taxes.