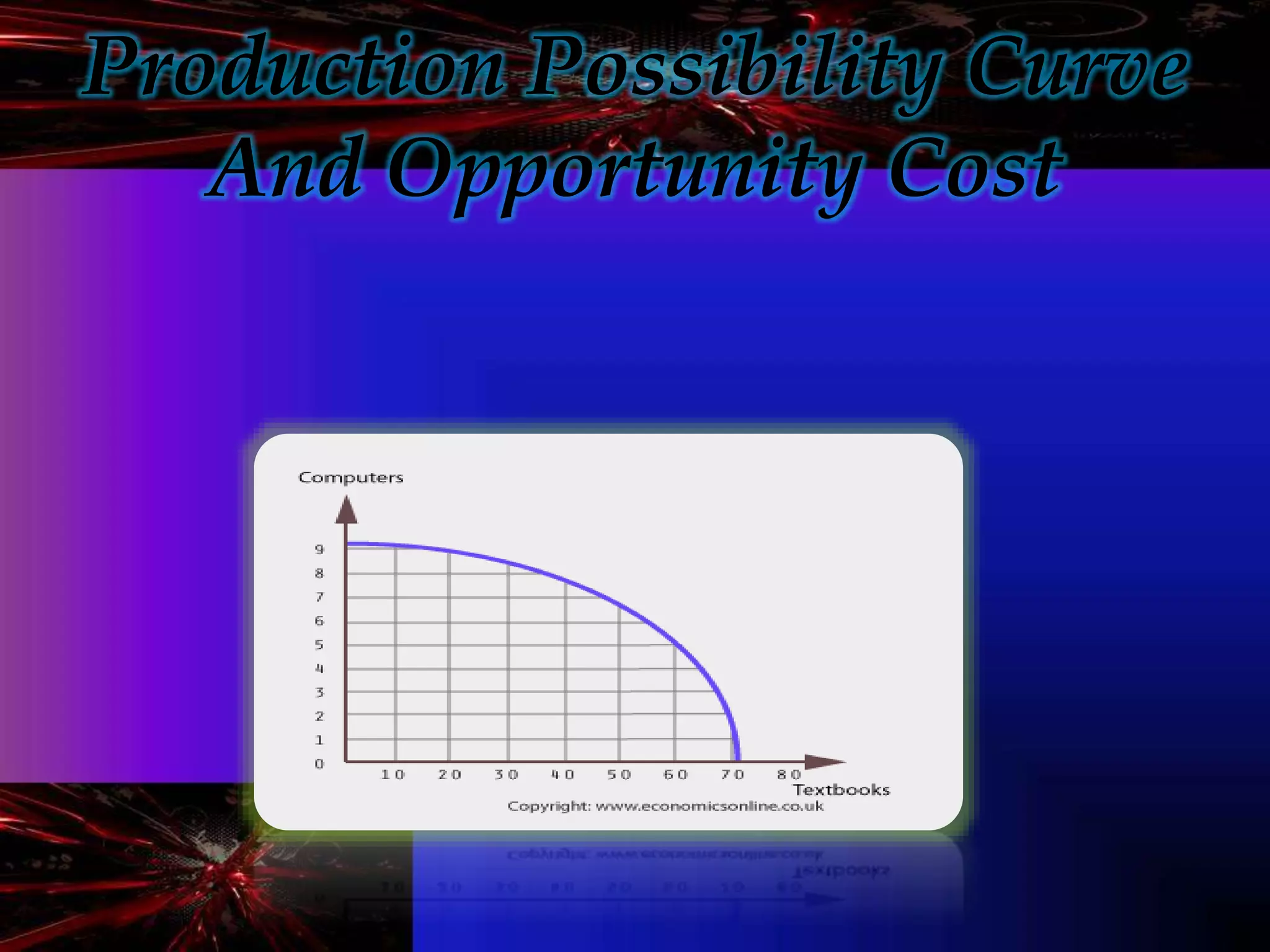
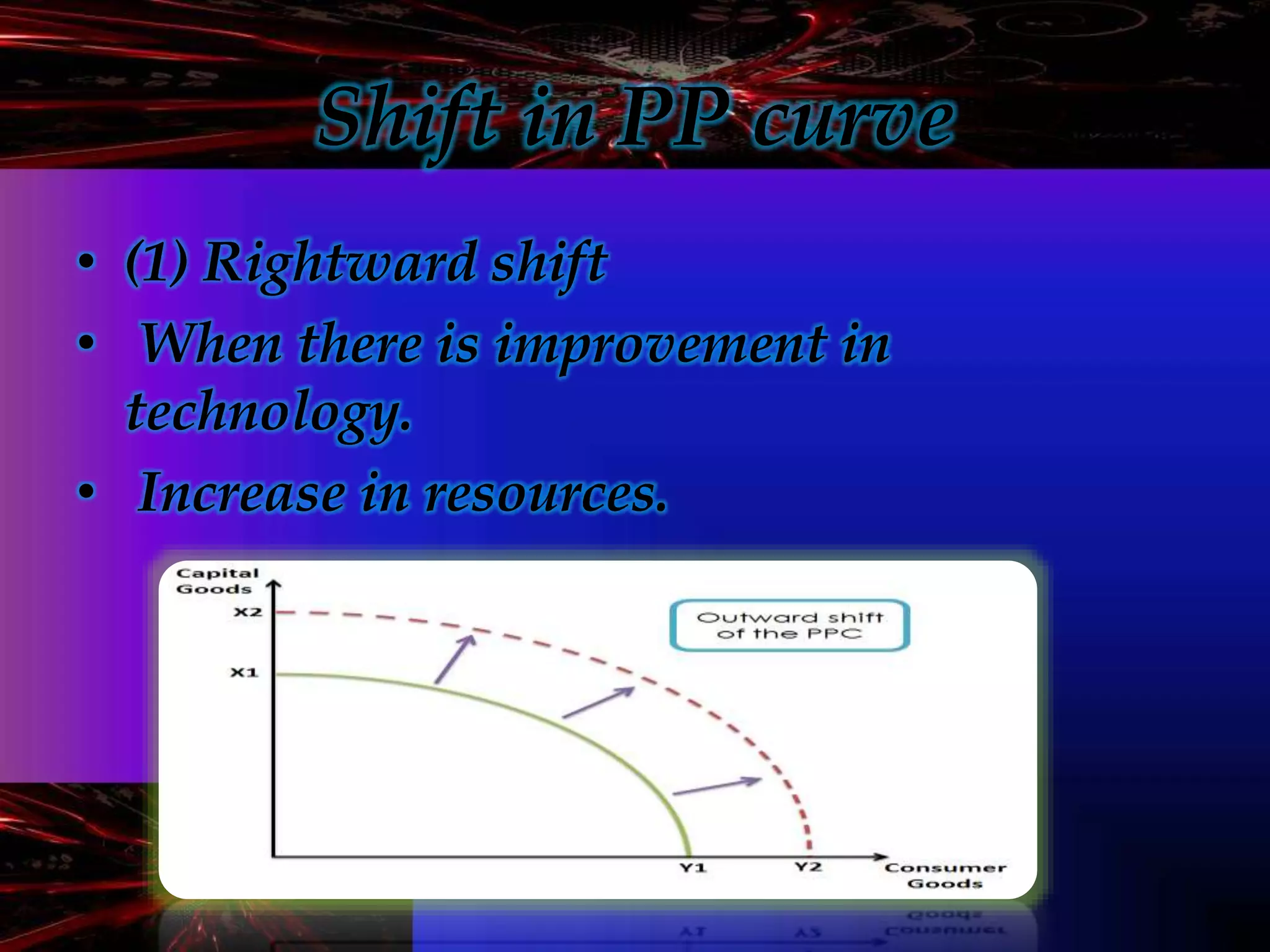
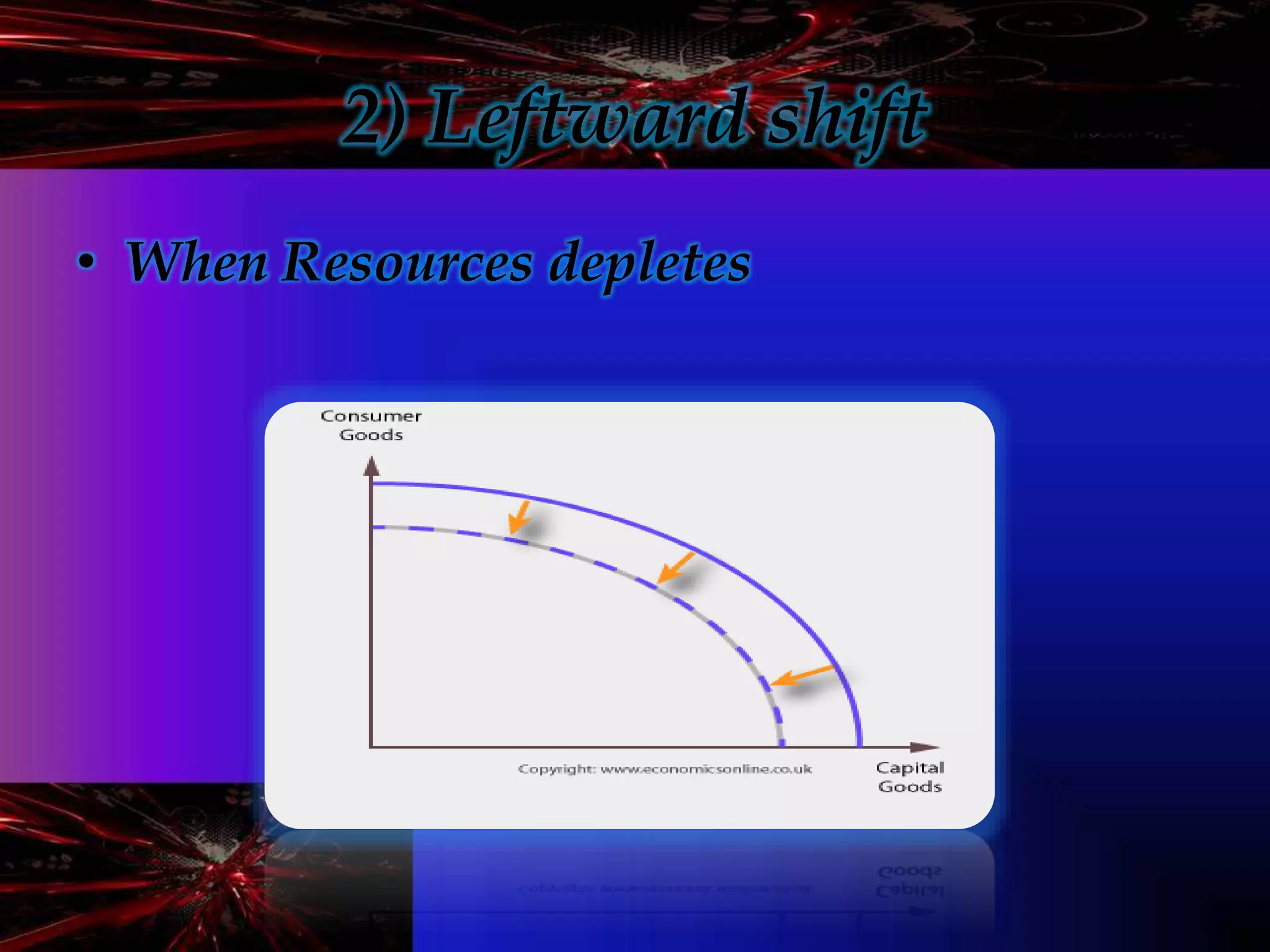
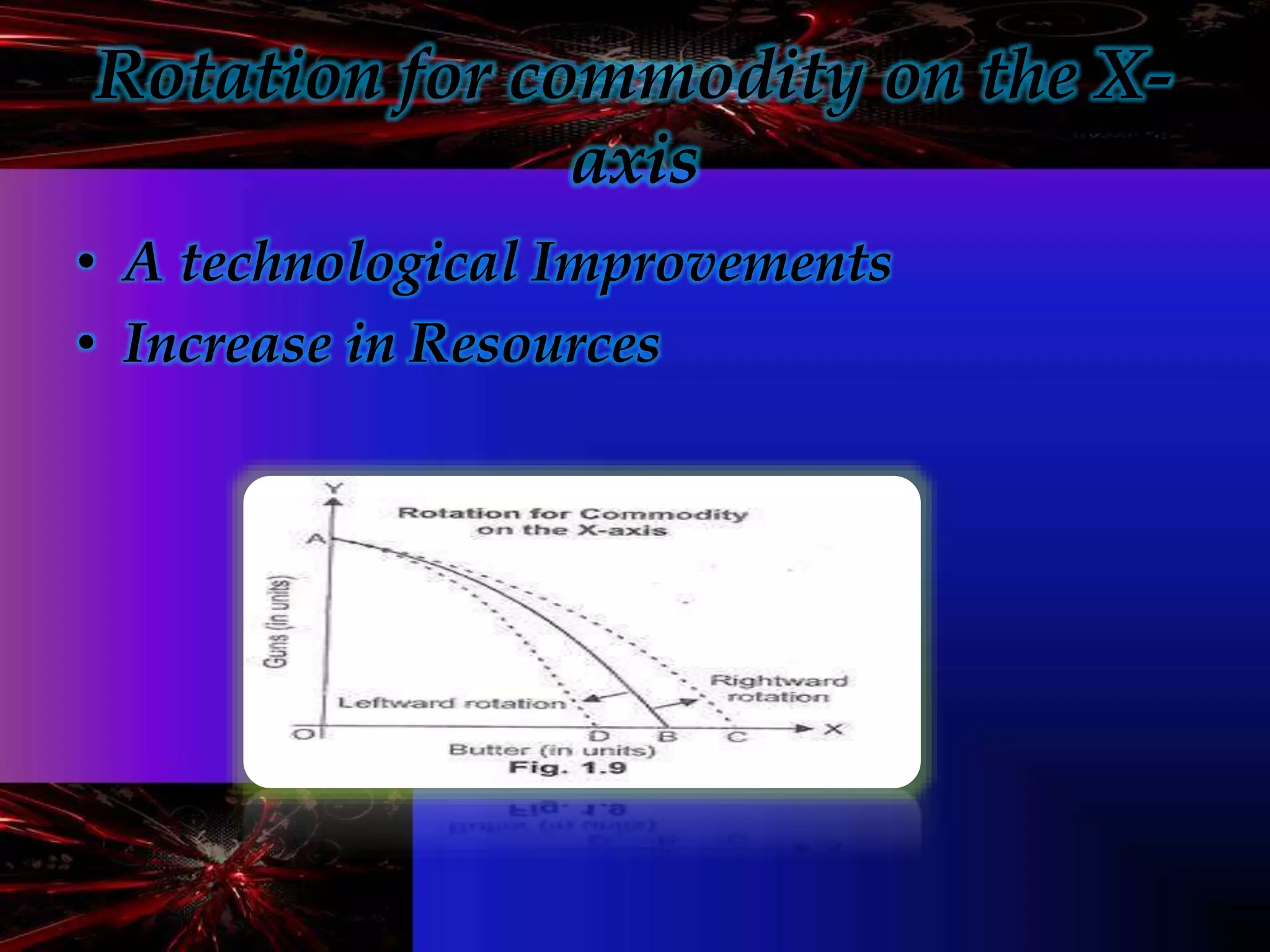
- Microeconomics is the study of individual units in an economy such as consumers and producers. It examines how scarce resources are allocated among competing ends.
- An economy is a system by which people obtain their living. There are three main types of economies: capitalist/market economies where production is privately owned, socialist/planned economies where production is centrally planned by the government, and mixed economies that have aspects of both.
- In a market economy, private individuals own resources and means of production, while in a planned economy the government owns and controls production. The key economic problem arises from scarcity of resources relative to unlimited wants, forcing choices between alternative uses of limited resources.