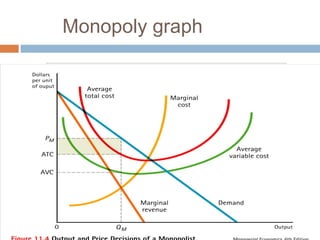
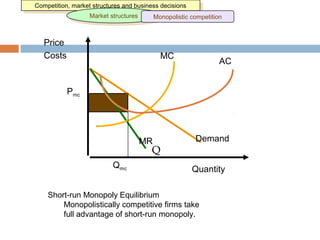
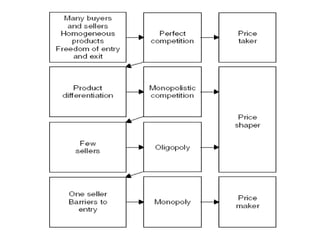
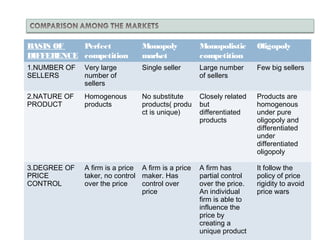
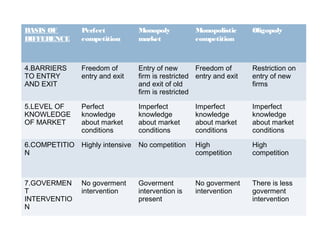
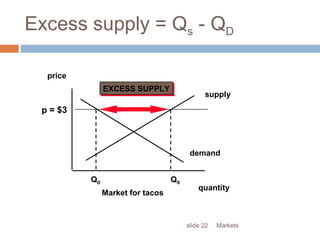
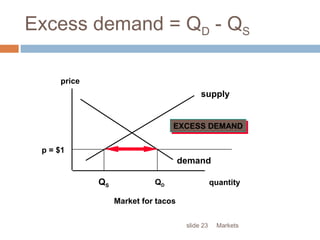
This document provides an overview of market structure and the different types of market structures. It discusses the key factors used to classify market structures, including the number of buyers and sellers, product differentiation, barriers to entry and exit, and level of competition. It then describes the characteristics of four main market structures: perfect competition, monopoly, monopolistic competition, and oligopoly. The document compares the differences between these market structures and provides examples of each. It also discusses price determination in markets and the concept of equilibrium price.