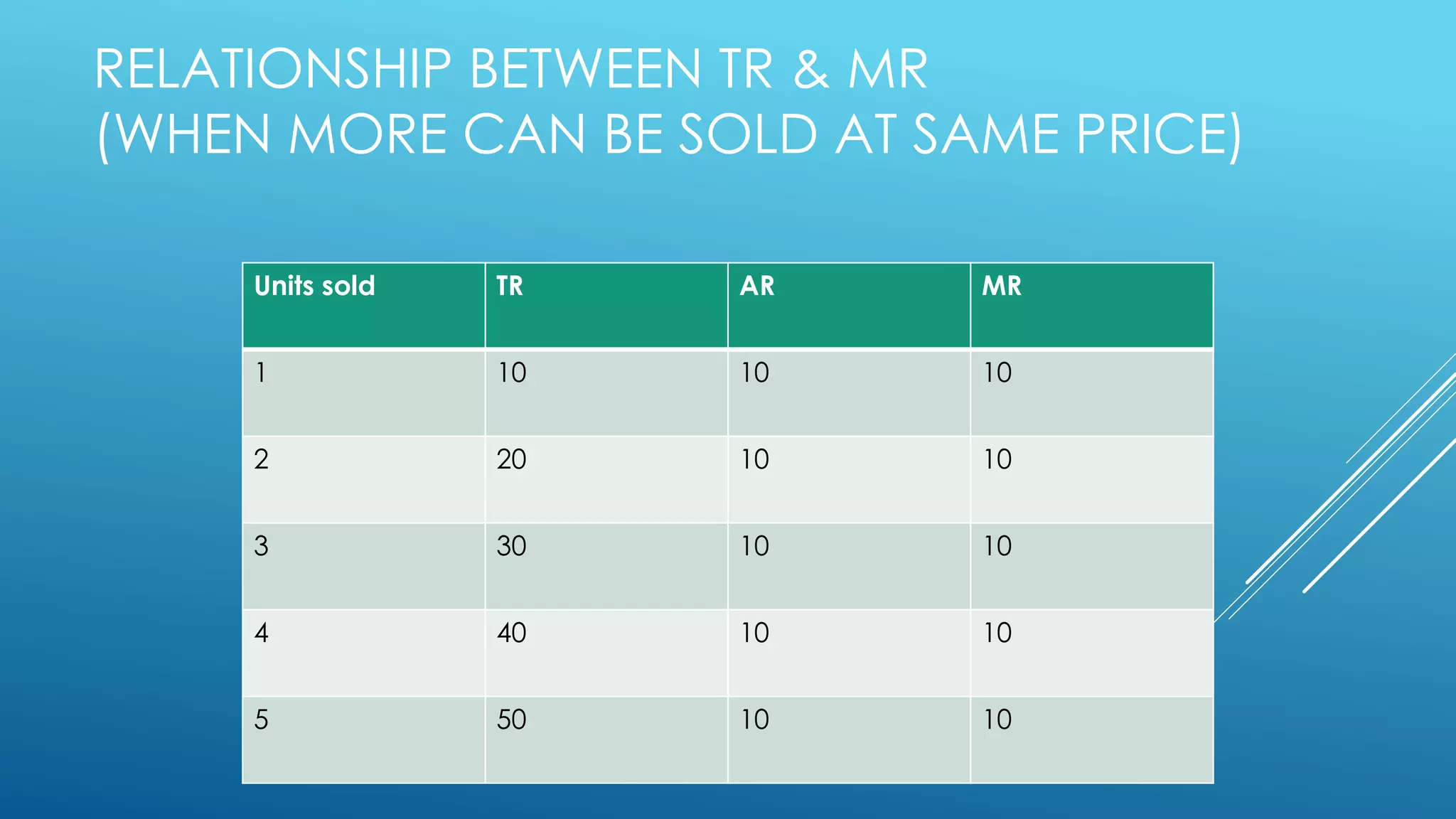
This document discusses concepts related to revenue. It defines total revenue as the sum total of money received from sales of output. Total revenue equals price multiplied by quantity. Marginal revenue is the change in total revenue from selling one more unit, and is calculated as the change in total revenue divided by the change in quantity. Average revenue is total revenue divided by quantity. Tables and graphs are presented showing the relationships between total revenue, marginal revenue, and average revenue as quantity changes. It is noted that total revenue increases at a diminishing rate as marginal revenue declines.