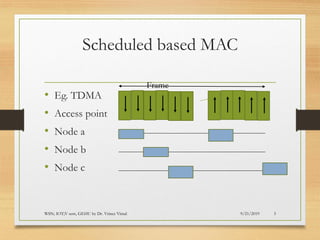
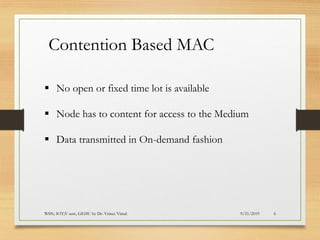
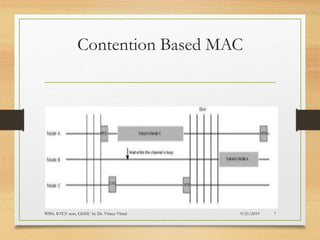
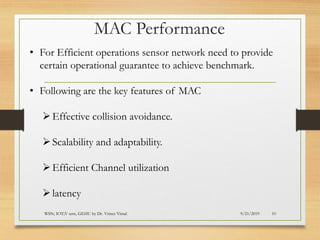
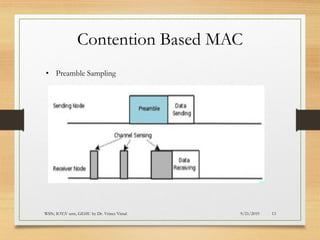
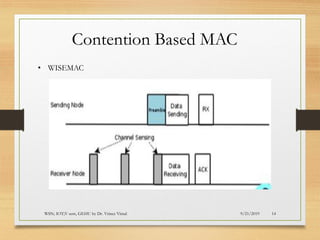
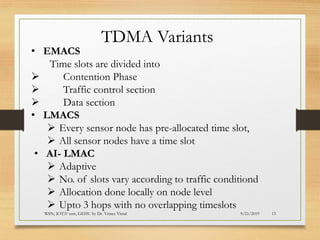
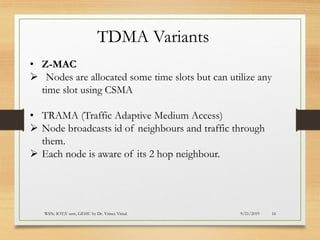
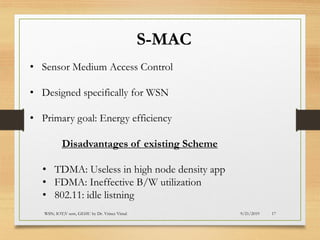
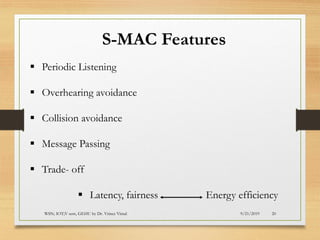
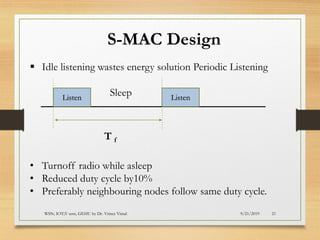
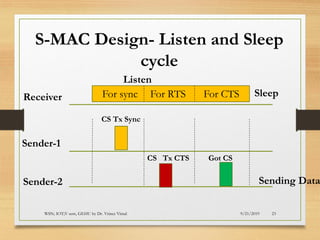
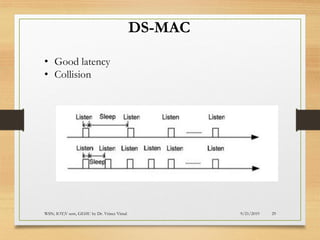
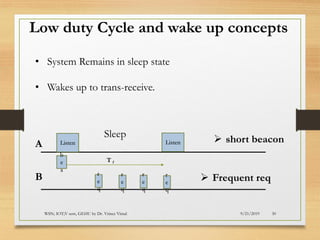
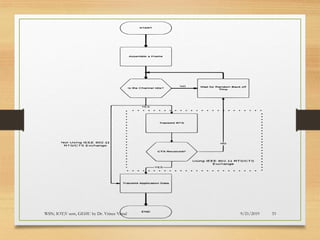
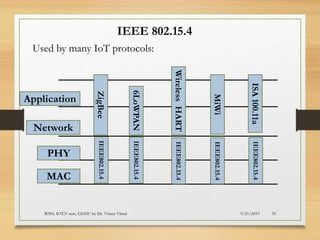
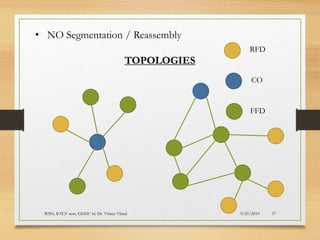
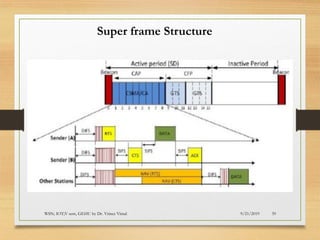
The document presents an in-depth analysis of Medium Access Control (MAC) protocols for Wireless Sensor Networks (WSN), focusing on their classification into scheduled-based and contention-based MAC. Key MAC protocols discussed include S-MAC, T-MAC, and various Time Division Multiple Access (TDMA) variants, emphasizing energy efficiency and network performance. Additionally, it covers the IEEE 802.15.4 MAC protocol and Zigbee's application in IoT systems.