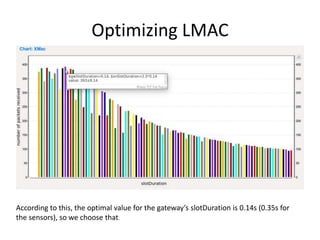
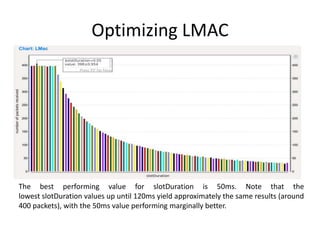
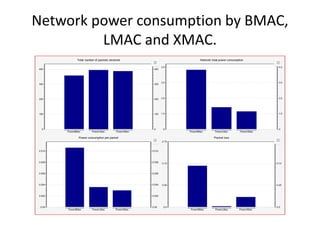
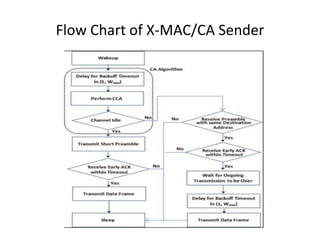
This document provides a progress report on research being conducted on energy management in wireless sensor networks using a modified MAC protocol. The report details work done so far, including modeling MAC protocols in OMNeT++, simulation results comparing BMAC, LMAC, and XMAC, and ongoing work to avoid collisions during packet transmission to improve energy efficiency. Future work includes further optimizing the modified MAC protocol and publishing results in peer-reviewed journals.




![Introduction to MAC protocols
• There are 2 types of protocols used to communicate the channels:
• TDMA based: In a TDMA based approach; time will be divided into time
slots, which will help the nodes to move their data without lavishing
energy of transmission. Only one time slot is assigned to every node [3].
• CSMA based: CSMA is a MAC convention wherein a node will check for
absence of an signal before transmitting.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/progress12-221130105551-ee0e6d44/85/PROGRESS-1-2-ppt-6-320.jpg)













![REFERENCES
• [1] V. Bharghavan, A. Demers, S. Shenker, and L. Zhang.MACAW:AMediaAccess
Protocol forWireless LAN’s.In ACMSIGCOMM1994, pages 212–225, ondon,
UK,August 31–September 2 1994.
• [2] A. Cerpa, N. Busek, and D. Estrin. SCALE: A tool for Simple Connectivity
Assessment in Lossy Environments. Technical report, CENS-TR-21, September2003.
• [3] L. Girod, J. Elson, A. Cerpa, T. Stathopoulos, N. Ra-manathan, and D. Estrin.
Emstar: a software environment for developing and deploying wireless sensor
networks. In Proceedings of the 2004 USENIX Technical Conference, Boston,MA,
2004. USENIX Association.
• [4] L. Girod, T. Stathopoulos, N. Ramanathan, J. Elson, D.Estrin,E.Osterweil, andT.
Schoellhammer. Tools for deployment and simulation of heterogeneous sensor
networks. In Proceedings of SenSys 2004, November 2004.
• [5] J. Hill, R. Szewczyk, A. Woo, S. Hollar, D. Culler, and K. Pister. System architecture
directions for networked sensors. In Proceedings of the Ninth International
Conference on Arhitectural Support for Programming Languages andOperating
Systems (ASPLOS-IX), pages 93 104, Cambridge,MA, USA, November 2000. ACM.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/progress12-221130105551-ee0e6d44/85/PROGRESS-1-2-ppt-26-320.jpg)
![• [6] C. T. Inc. Mica2 wireless measurement system datasheet,
http://www.xbow.com/products/product pdf files /datasheets /wireless/6020-
0042-03 a mica2.pdf.
• [7] V. Jacobson. Congestion avoidance and control. ACM Computer Communication
Review; Proceedings of the Sigcomm’88 Symposiumin tanford,CA,August, 1988,
18, 4:314–329, 1988.
• [8] D. Katabi, M. Handley, and C. Rohrs. Internet congestion control for future high
bandwidth-delay product environments, 2002.
• [9] A.Mainwaring,D. Culler, J. Polastre, R. Szewczyk, and J. Anderson. Wireless
sensor networks for habitatmon itoring. In Proceedings of the 1st ACM
international workshop onWireless sensor networks and applications, pages 88–
97. ACMPress, 2002.
• [10] T. Stathopoulos, J.Heidemann, andD.Estrin. Aremote code update mechanism
for wireless sensor networks. Technical Report CENS-TR-30, University of Califor
nia,LosAngeles,Center forEmbeddedNetworkedComputing, November 2003.
• [11] T. van Dam and K. Langendoen. An adaptive energy efficient mac protocol for
wireless sensor networks. In Proceedings of the first international conference on
Embedded networked sensor systems, pages 171–180. ACM Press, 2003.
• [12] A. Woo, T. Tong, and D. Culler. Taming the underlying challenges of reliable
multihop routing in sensor networks. In Proceedings of the first international
conference on Embedded networked sensor systems, pages 14–27. ACMPress,
2003.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/progress12-221130105551-ee0e6d44/85/PROGRESS-1-2-ppt-27-320.jpg)