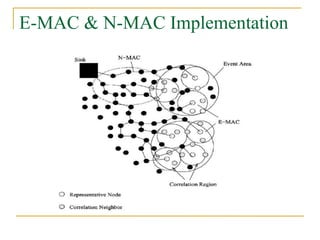
1. The document proposes a correlation-based collaborative MAC protocol called SCC-MAC to reduce energy consumption in wireless sensor networks.
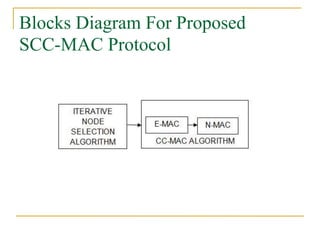
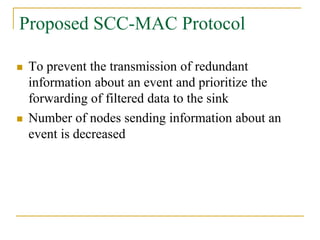
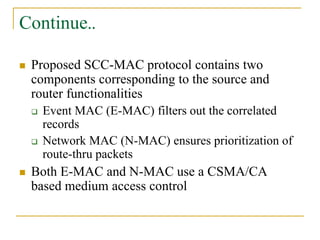
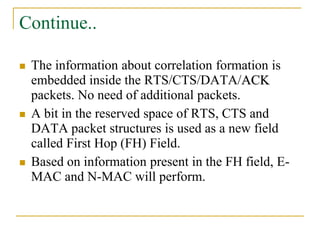
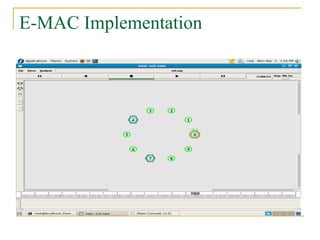
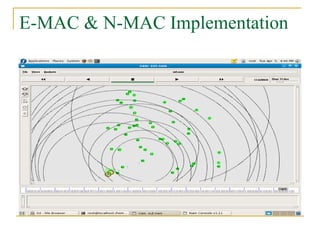
2. SCC-MAC contains two components - E-MAC filters out redundant event information while N-MAC prioritizes forwarding of filtered data to the sink.
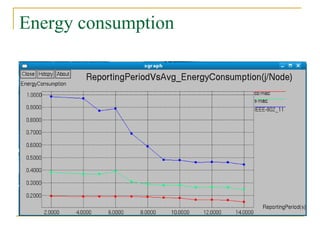
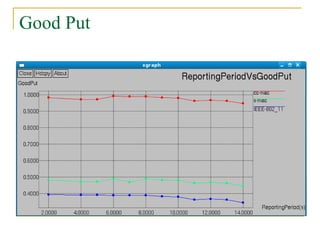
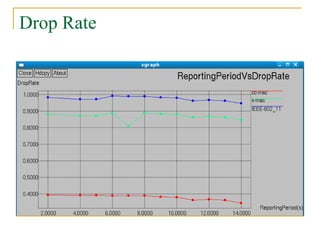
3. Simulations show that SCC-MAC achieves significant gains in energy consumption, goodput, and packet drop rate compared to existing MAC protocols by allowing only a subset of sensor nodes to transmit data.




![Reference
[1]“Spatial Correlation-Based Collaborative Medium Access Control in
Wireless Sensor Networks”, Mehmet C. Vuran, Member, IEEE, and Ian F.
Akyildiz, Fellow, IEEE,2006
[2] “An Adaptable Energy-Efficient Medium Access Control Protocol for
Wireless Sensor Networks”, Justin T. Kautz, Barry E. Mullins, Rusty O.
Baldwin, Scott R. Graham, 2007
[3] “Energy Efficient Cluster header Selection Algorithm in WSN”, Inbo
Sim, KoungJin Choi, KoungJin Kwon and Jaiyong Lee, 2008
[4] “On the Adaptivity of today’s Energy-Efficient MAC Protocols under
varying Traffic Conditions”, Philipp Hurni, Torsten Braun, 2009
[5] “Energy Efficient and Delay Optimized TDMA Scheduling for
Clustered Wireless Sensor Networks”, Liqi Shi and Abraham O. Fapojuwo,
2009](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mmm-221109062114-73e88c6b/85/mmm-ppt-22-320.jpg)
![Continue..
[6] “Energy Efficient Cross-Layer MAC Protocol for Wireless Sensor
Networks”, Bouabdellah KECHAR, Ahmed LOUAZANI, Larbi SEKHRI,
Mohamed Faycal KHELFI, 2008
[7] “Energy Efficient Token Based MAC Protocol for Wireless Sensor
Networks”, Soumya Ray, ,Subhasis Dash ,Nachiketa Tarasia ,Anuja Ajay,
Amulya Ratan Swain, 2011
[8] “Wireless Sensor Networks:Delay Guarentee and Energy Efficient
MAC Protocols”, Marwan Ihsan Shukur, Lee Sheng Chyan, Vooi Voon
Yap, 2009
[9] “ M. Gastpar and M. Vetterli, “Source-channel communication in
sensor networks,” Proc. 2nd Int. Workshop on Information Processing in
Sensor Networks (IPSN’03), vol. 219, pp. 162–177, 2003.
[10] M. C. Vuran, Ö. B. Akan, and I. F. Akyildiz, “Spatio-temporal
correlation: theory and applications for wireless sensor networks,” Comput.
Netw. J. (Elsevier), vol. 45, no. 3, pp. 245–259, Jun. 2004
](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mmm-221109062114-73e88c6b/85/mmm-ppt-23-320.jpg)
![Continue..
[11] Mehmet C. Vuran, Member and Ian F. Akyildiz, Fellow,” Spatial
Correlation-Based Collaborative Medium Access Control in Wireless
Sensor Networks”,2004
[12] K. A. Arisha, M. A. Youssef, and M. Y. Younis, “Energy-aware
TDMA-based MAC for sensor networks,” Comput. Netw. J. (Elsevier), vol.
43, no. 5, pp. 539–694, Dec. 2003.
[13] S. Bandyopadhyay and E. J. Coyle, “Spatio-temporal sampling rates
and energy efficiency in wireless sensor networks,” in Proc. IEEE
INFOCOM, Mar. 2004, vol. 3, pp. 1728–1739.
[14] “Power, spatio-temporal bandwidth, and distortion in large sensor
networks,” IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun., vol. 23, no. 4, pp. 745–754, Apr.
2005.
[15] W. Ye, J. Heidemann, and D. Estrin, “Medium access control with
coordinated adaptive sleeping for wireless sensor networks,” IEEE/ACM
Trans. Netw., vol. 12, no. 3, pp. 493–506, Jun. 2004.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mmm-221109062114-73e88c6b/85/mmm-ppt-24-320.jpg)
