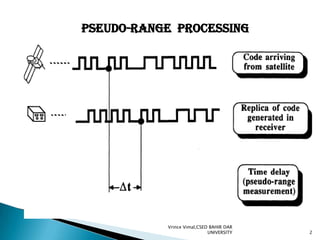
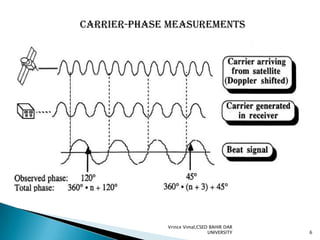
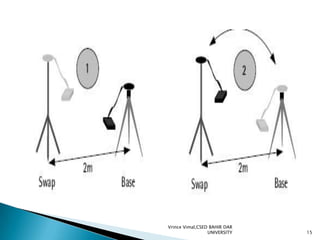
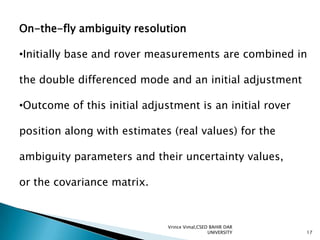
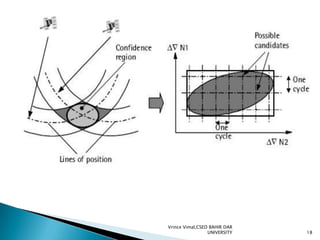
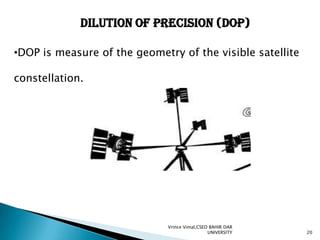
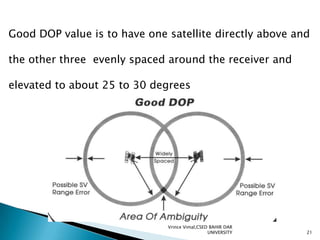
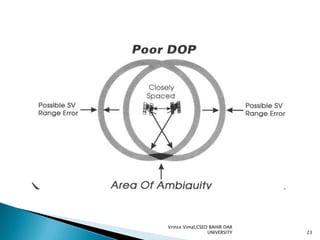
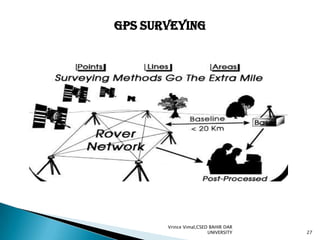
The document discusses GPS processing techniques, including pseudo-range processing and carrier-phase measurements. Pseudo-ranges are a measure of distance between a GPS receiver and satellite based on the time shift needed to align code signals. Carrier-phase measurements provide even higher precision but require resolving the integer cycle ambiguity. Methods for ambiguity resolution include receiver initialization, antenna swapping, and on-the-fly processing. Good satellite geometry as measured by dilution of precision (DOP) helps improve positioning accuracy. Applications discussed include surveying, geographical positioning, control networks, and determining heights and the geoid.