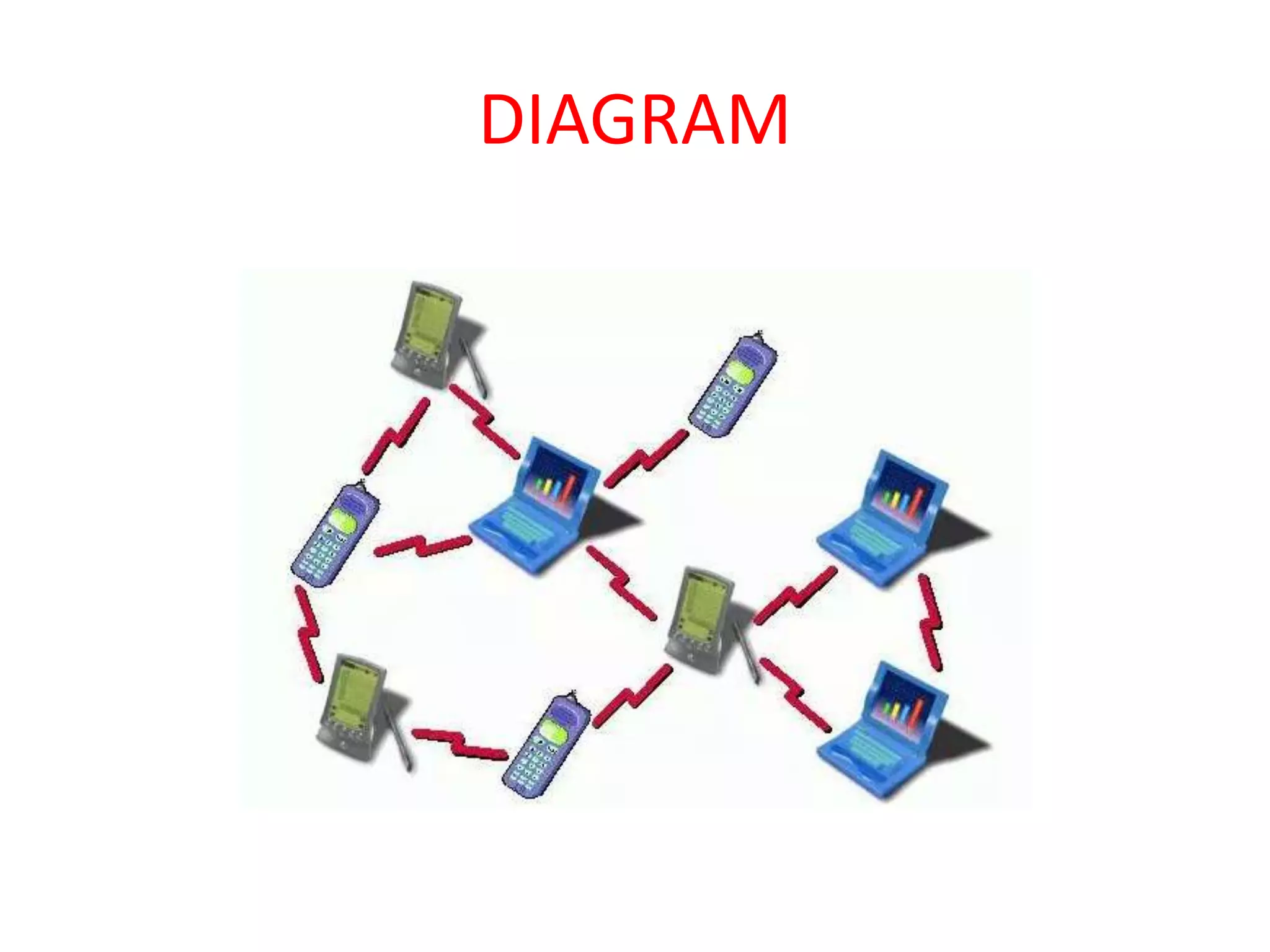
MANET is a type of mobile ad hoc network that is self-configuring and infrastructureless, allowing mobile devices to connect without wires. Nodes in a MANET can join or leave the network freely, making the network topology dynamic. Each node acts as both a host and router to forward data. MANETs support multi-hop routing to allow communication between nodes out of direct wireless range. They offer advantages like scalability, low cost, and access to information anywhere but also face challenges like variable wireless link quality, low data rates, and partitioned networks due to node movement.