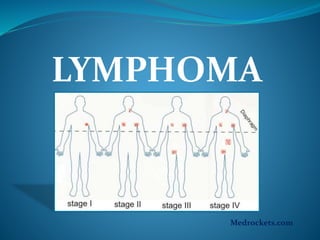
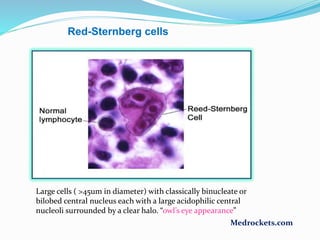
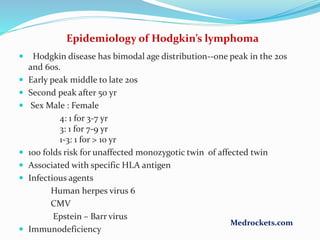
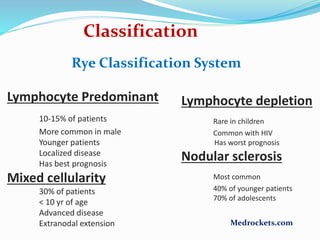
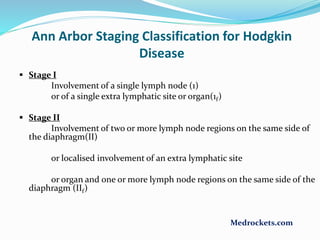
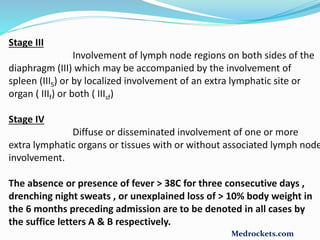
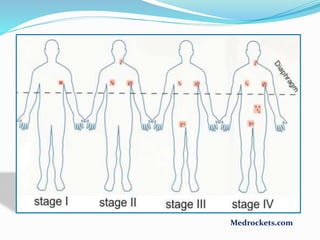
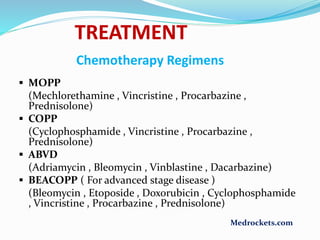
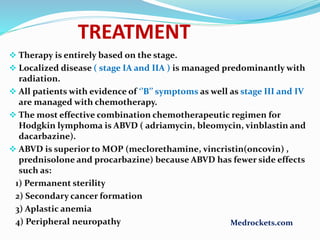
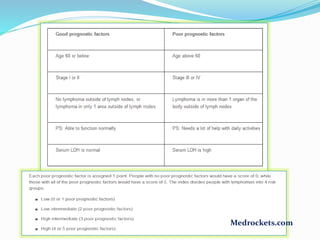
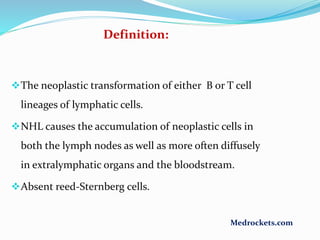
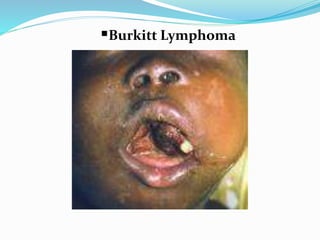
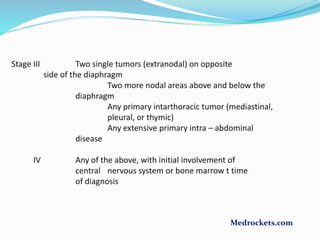
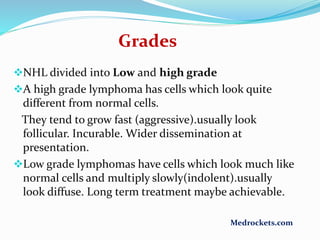
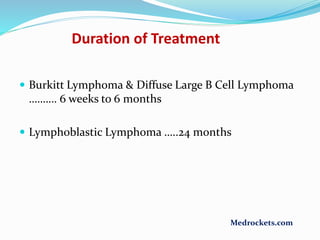
Lymphoma refers to tumors of the lymphatic system, specifically lymphocytes and their precursor cells. The two main types are Hodgkin's lymphoma and non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. Hodgkin's lymphoma is characterized by the presence of Reed-Sternberg cells. It commonly affects lymph nodes in a stepwise fashion and has a bimodal age distribution. Non-Hodgkin's lymphoma can involve both B and T cells and often spreads more diffusely beyond lymph nodes. Diagnosis involves an excisional lymph node biopsy. Treatment depends on disease stage and may involve chemotherapy, with or without radiation therapy. Prognosis can be determined using factors in the International Prognostic Index.