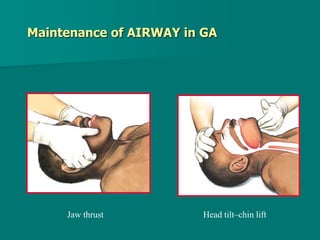
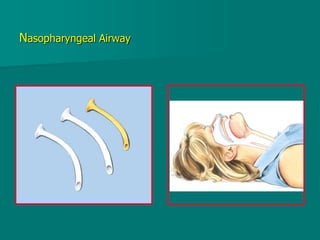
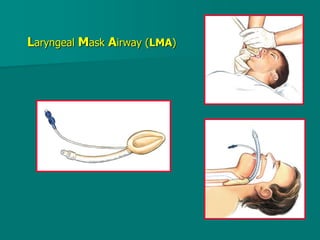
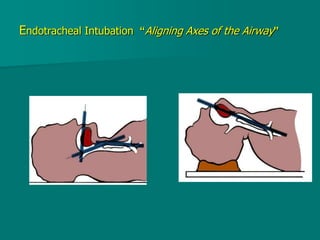
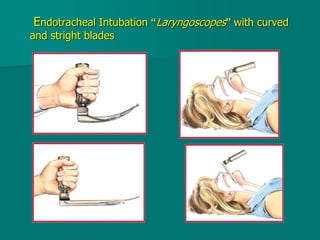
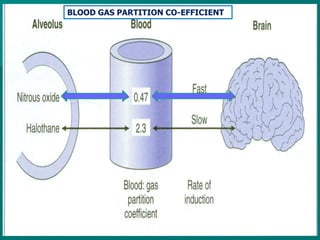
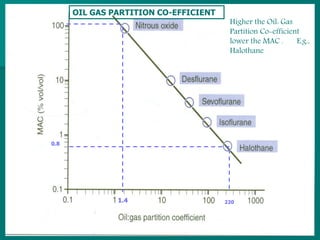
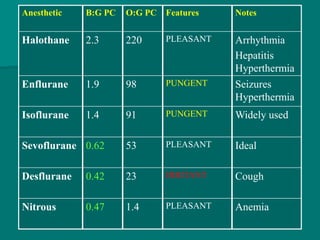
General anesthesia involves administering anesthetic agents to induce a reversible state of unconsciousness and loss of pain sensation. It progresses through four stages from analgesia to respiratory and vasomotor paralysis. Anesthetic agents act primarily by potentiating the GABA receptor or inhibiting the NMDA receptor. They can be administered via various routes including intravenous, inhalation, rectal or intramuscular injection to produce depression of the brain. Common inhalational agents include nitrous oxide, halothane, sevoflurane and desflurane while intravenous agents used for induction and maintenance include propofol, thiopental and ketamine. General anesthesia provides unconsciousness, analgesia, amnesia and muscle relaxation during surgery.