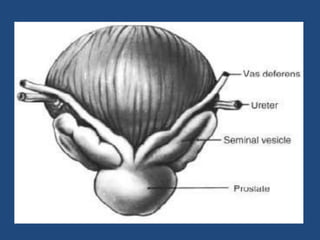
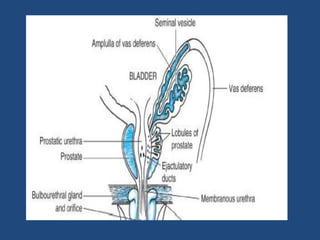
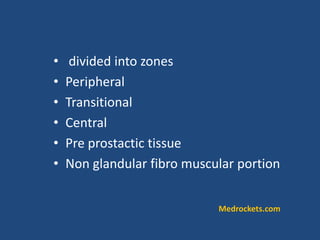
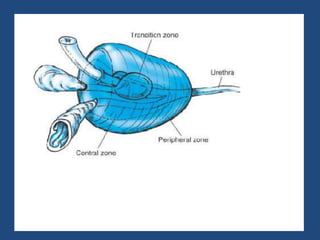
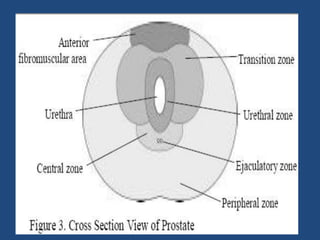
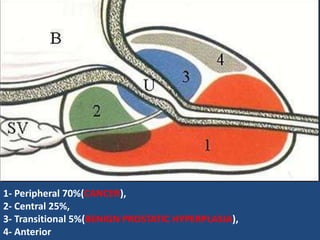
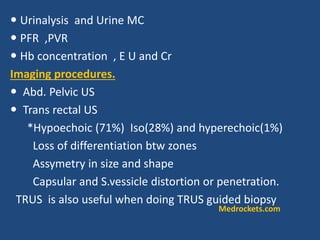
Prostatic cancer is the most commonly diagnosed malignancy in men beyond middle age. The prostate gland is located below the bladder and surrounds the urethra. Cancer usually develops in the peripheral zone and can spread locally or metastasize through the lymphatic system or bloodstream, commonly to bone. Diagnosis involves a PSA test, digital rectal exam, and biopsy. Treatment options depend on stage but may include surgery, radiation, hormone therapy, or active surveillance. Prognosis depends on stage and grade, with early-stage disease having an excellent long-term survival.