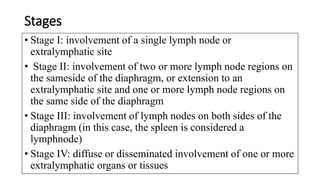
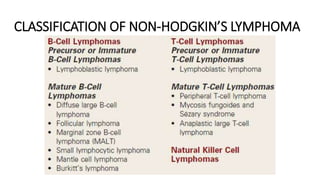
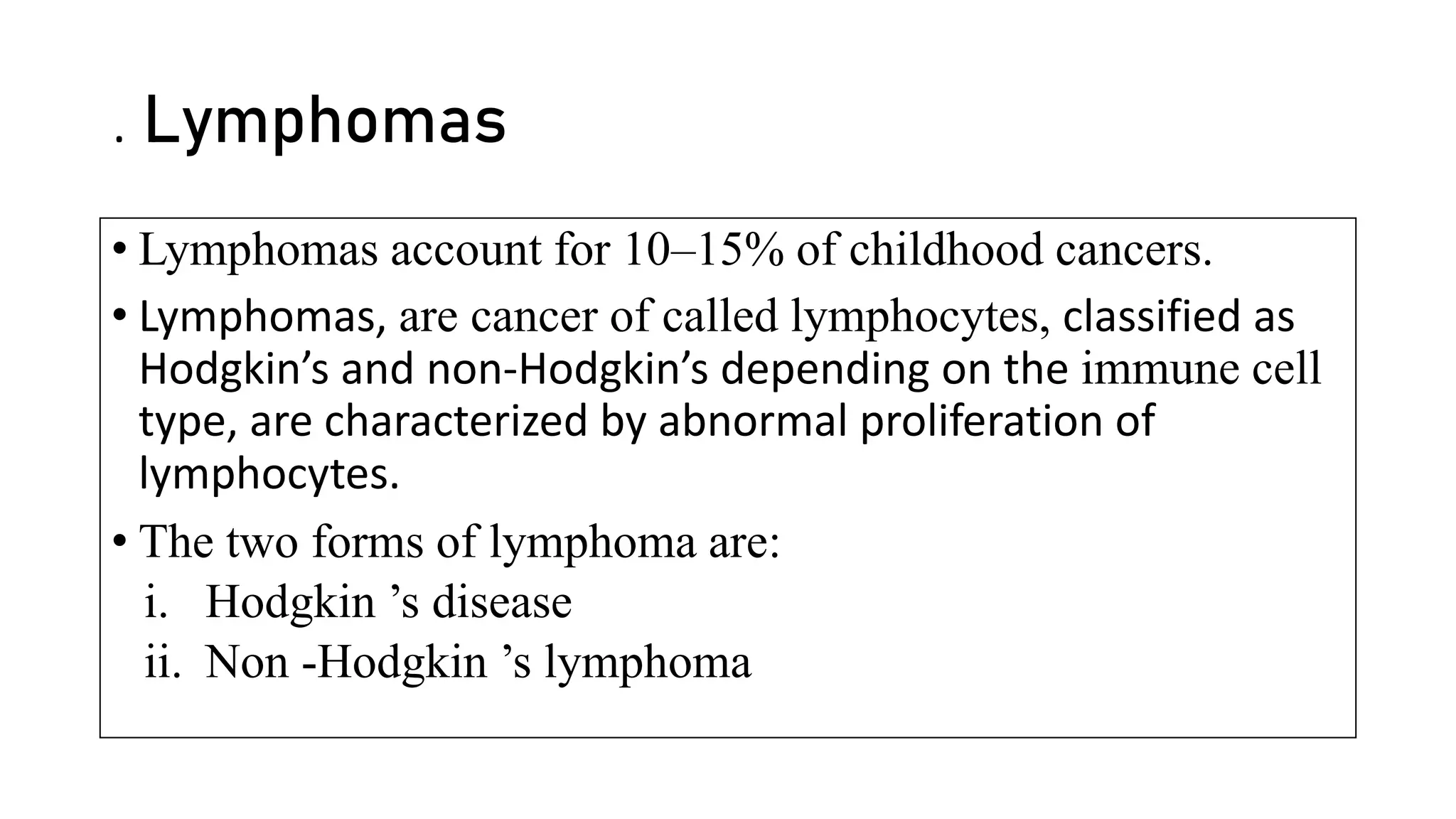
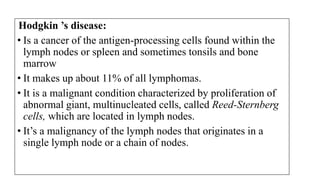
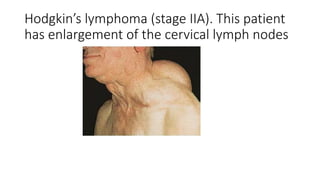
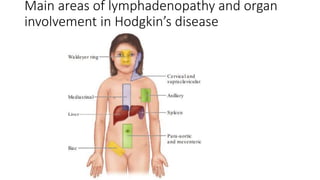
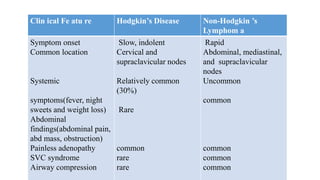
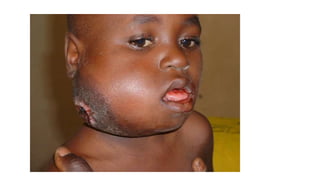
Lymphomas account for 10-15% of childhood cancers and are cancers of lymphocytes. The two main forms are Hodgkin's lymphoma and non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. Hodgkin's lymphoma is characterized by abnormal Reed-Sternberg cells in lymph nodes and commonly presents with painless lymphadenopathy. It has a bimodal age distribution and is treated with chemotherapy and/or radiation. Non-Hodgkin's lymphoma is more aggressive and heterogeneous, involving lymphocytes at different developmental stages. It has a variety of clinical presentations depending on the site of spread and commonly presents with widespread disease.





![CONT’D
• The patient may notice weight loss, fatigue, weakness, fever, chills,
tachycardia, or night sweats.
• A group of initial findings including fever (in excess of 100.4° F [38°
C]), drenching night sweats, and weight loss (exceeding 10% in 6
months) are termed B symptoms and correlate with a worse
prognosis.
• After the ingestion of even small amounts of alcohol, individuals with
Hodgkin’s lymphoma may complain of a rapid onset of pain at the site
of disease. The cause for the alcohol-induced pain is unknown.
• Generalized pruritus without skin lesions may develop.
• Cough, dyspnea, stridor, and dysphagia may all reflect mediastinal
node involvement.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lymphoma-230226112154-e0cdd33e/85/LYMPHOMA-pptx-14-320.jpg)