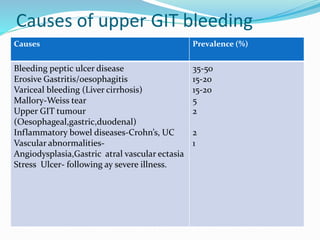
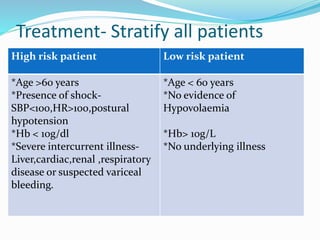
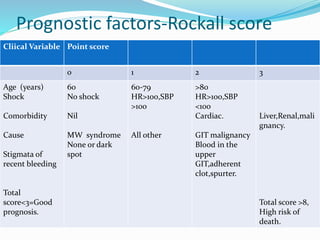
This document provides an outline of a lecture on upper gastrointestinal tract bleeding. It begins with definitions and discusses the epidemiology, causes, clinical presentation, diagnosis, treatment, complications, and prognosis of upper GI bleeding. The most common causes are bleeding peptic ulcers, erosive gastritis/esophagitis, and variceal bleeding from liver cirrhosis. The clinical presentation depends on features of blood loss and the underlying cause. Diagnosis involves history, physical exam, and investigations like blood tests, abdominal ultrasound, and upper endoscopy. Treatment involves resuscitation, transfusions, medications, and procedures depending on the identified cause. Complications can be from blood loss, treatment, or the underlying condition. Pro