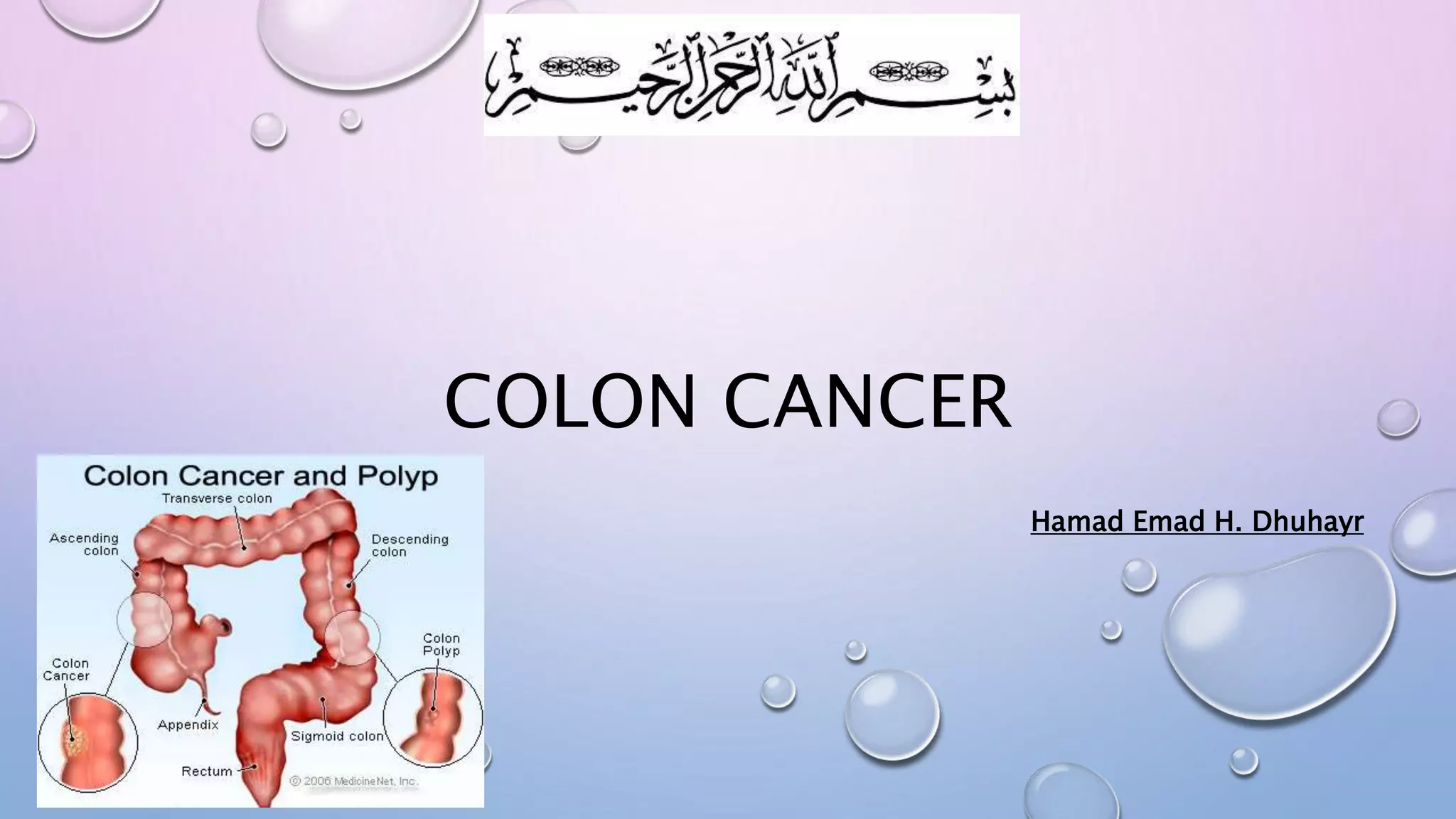
Colon cancer typically begins as a noncancerous polyp in the lining of the colon or rectum and can become cancerous over time. Risk factors include age, family history, diet high in red meat and saturated fats, obesity, smoking, and alcohol use. Screening is important, as early detection improves outcomes - average risk adults should be screened beginning at age 50. Colon cancer is staged based on how far it has spread, with treatment options including surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation depending on the stage. While early stage cancers can often be cured with surgery alone, advanced cancers are difficult to treat and the goals shift to slowing growth and managing symptoms.