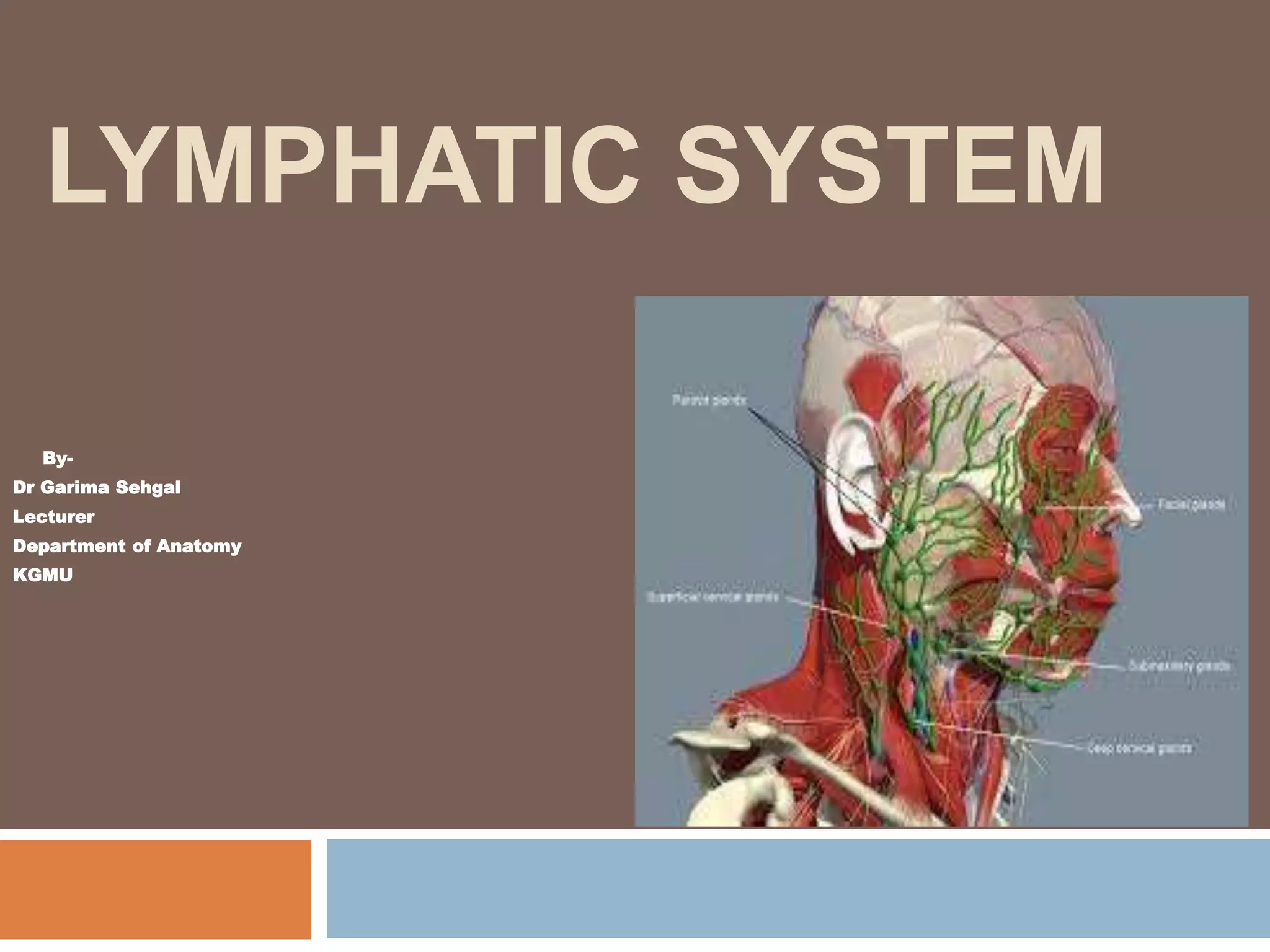
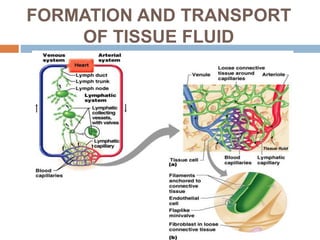
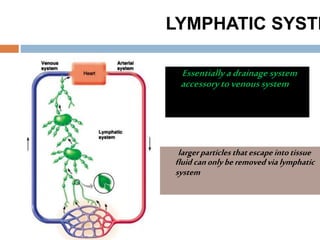
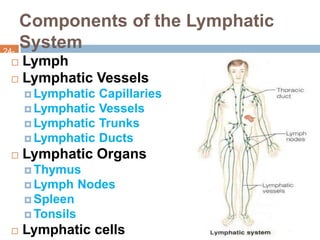
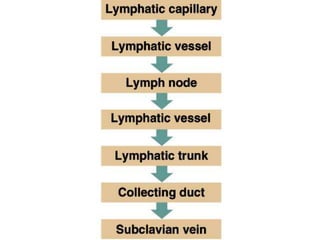
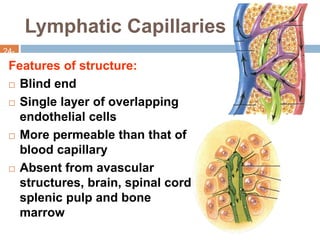
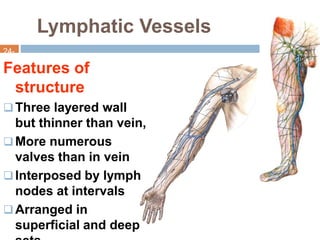
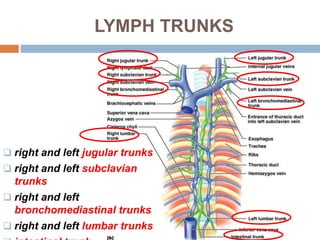
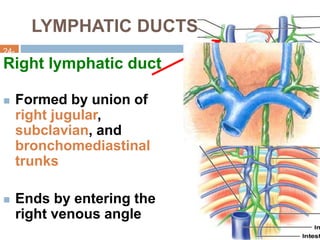
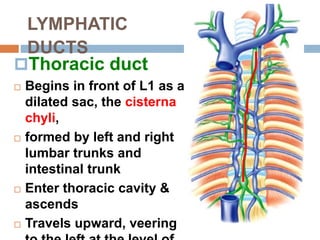
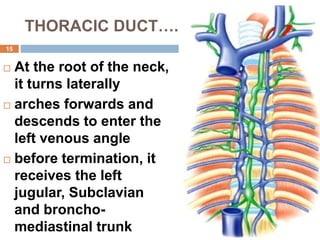
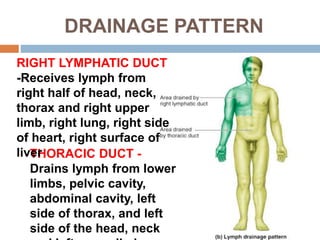
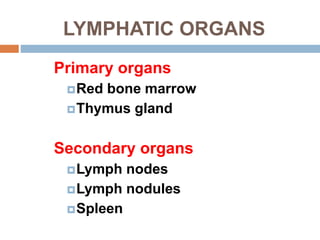
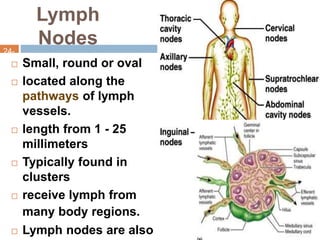
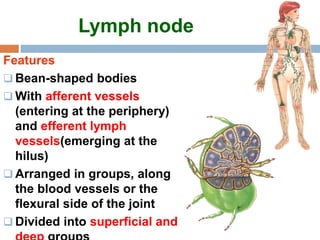
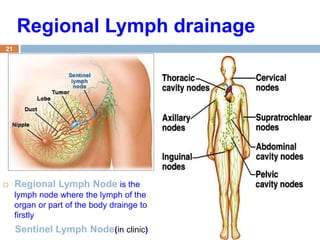
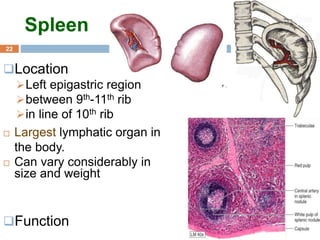
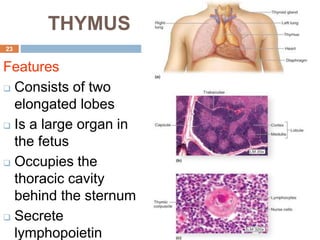
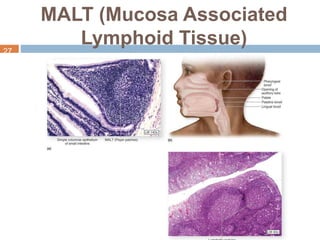
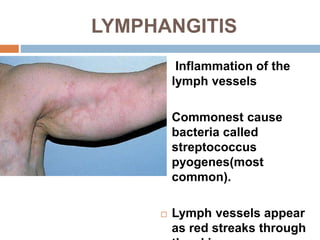
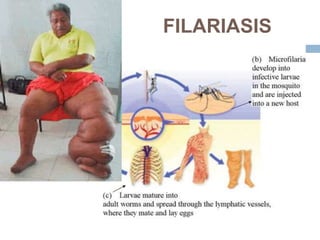
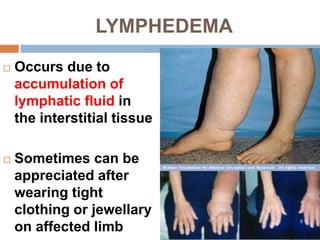
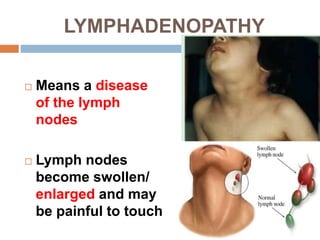
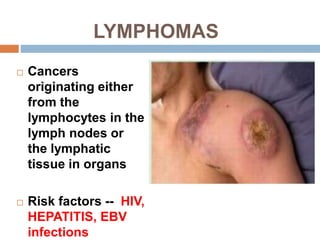
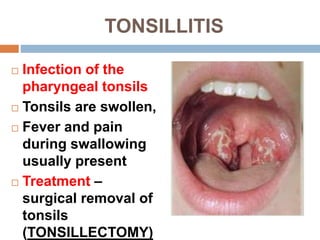
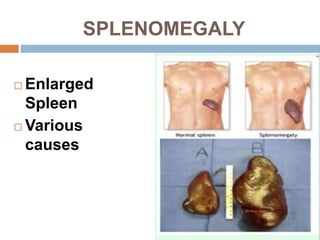
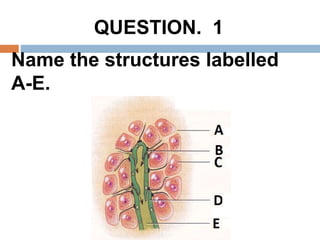
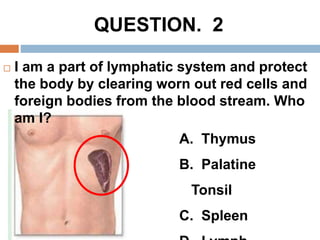
The document provides information about the lymphatic system. It discusses that the lymphatic system is an accessory drainage system to the venous system that transports lymph fluid and absorbs excess interstitial fluid. The main components of the lymphatic system include lymph, lymphatic vessels (capillaries, vessels, trunks, and ducts), lymphatic organs (thymus, lymph nodes, spleen, tonsils), and lymphatic cells. The key functions of the lymphatic system are to reabsorb excess interstitial fluid, transport dietary lipids, and aid in immune responses and lymphocyte development. The document also discusses various lymphatic structures and their features in detail.